Activity-dependent differential transmitter release in mouse adrenal chromaffin cells
- PMID: 16093382
- PMCID: PMC6725304
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2042-05.2005
Activity-dependent differential transmitter release in mouse adrenal chromaffin cells
Abstract
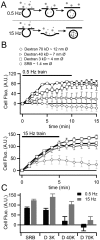
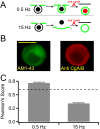
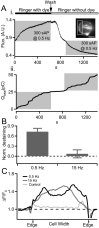
Chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla are a primary neuroendocrine output of the sympathetic nervous system. When stimulated, they secrete a host of transmitter molecules, including catecholamines and neuropeptides, through the fusion of dense core secretory granules with the cell surface. At basal firing rates, set by the sympathetic tone, chromaffin cells selectively release catecholamines at a modest rate. Stress-mediated sympathetic activation leads to elevated catecholamine secretion and also evokes neuropeptide release. Catecholamines and neuropeptides are copackaged in the same granules; thus, it is unclear how this activity-dependent differential transmitter release is achieved. In this report, we use electrophysiological, electrochemical, fluorescence, and immunocytochemical approaches to quantify transmitter release under physiological electrical stimulation at the single cell level. We provide data to show that chromaffin cells selectively release catecholamine under basal firing conditions but release both neuropeptides and catecholamines under conditions that match acute stress. We further show that this differential transmitter release is achieved through a regulated activity-dependent dilation of the granule fusion pore. Thus, chromaffin cells may regulate release of different transmitters through a simple size-exclusion mechanism.
Figures



References
-
- Albillos A, Dernick G, Horstmann H, Almers W, Alvarez de Toledo G, Lindau M (1997) The exocytotic event in chromaffin cells revealed by patch amperometry. Nature 389: 509-512. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez de Toledo G, Fernández-Chacón R, Fernández JM (1993) Release of secretory products during transient vesicle fusion. Nature 363: 554-558. - PubMed
-
- Angleson JK, Cochilla AJ, Kilic G, Nussinovitch I, Betz WJ (1999) Regulation of dense core release from neuroendocrine cells revealed by imaging single exocytotic events. Nat Neurosci 2: 440-446. - PubMed
-
- Aravanis AM, Pyle JL, Tsien RW (2003) Single synaptic vesicles fusing transiently and successively without loss of identity. Nature 423: 643-647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
