Bidirectional modulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation under stress and no-stress conditions in basolateral amygdala-lesioned and intact rats
- PMID: 16093390
- PMCID: PMC6725292
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0910-05.2005
Bidirectional modulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation under stress and no-stress conditions in basolateral amygdala-lesioned and intact rats
Abstract
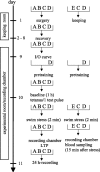
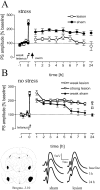
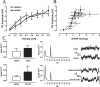
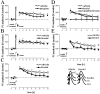
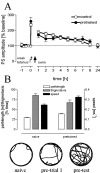
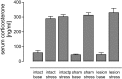
Hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) is widely considered as a cellular model for learning and memory formation. We have shown previously that protein synthesis-independent, early dentate gyrus (DG) LTP, lasting approximately 4-5 h, can be transformed into a late-LTP with a duration of > or = 24 h by a brief acute swim stress experience (high-stress condition). This reinforcement requires the activation of mineralocorticoid receptors and protein synthesis. The basolateral amygdala (BLA) is known to modulate glucocorticoid effects on the consolidation of spatial/contextual memory via a beta-adrenergic mechanism. Interestingly, hippocampal DG-LTP can also be indirectly modulated by beta-adrenergic and cholinergic/muscarinergic processes. Here, we show that the reinforcement of early-DG-LTP under high-stress conditions depends on the processing of novel spatial/contextual information. Furthermore, this reinforcement was blocked in BLA-lesioned animals compared with sham-operated and intact controls; however, it was not dependent on beta-adrenergic or cholinergic/muscarinergic receptor activation. In contrast, under low-stress conditions, the induction of late-LTP in BLA-lesioned animals is facilitated, and this facilitation, again, was dependent on beta-adrenergic activation. The data suggest that DG-LTP maintenance can be influenced by the BLA through different mechanisms: a short-lasting corticosterone-dependent and beta-adrenergic-independent mechanism and a long-lasting mechanism that facilitated hippocampal beta-adrenergic mechanisms.
Figures
References
-
- Abe K, Nakata A, Mizutani A, Saito H (1994) Facilitatory but nonessential role of the muscarinic cholinergic system in the generation of long-term potentiation of population spikes in the dentate gyrus in vivo. Neuropharmacology 33: 847-852. - PubMed
-
- Almaguer-Melian W, Martinez-Marti L, Frey JU, Bergado JA (2003) The amygdala is part of the behavioural reinforcement system modulating long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 119: 319-322. - PubMed
-
- Bergado JA, Almaguer-Melian W, Kostenko S, Frey S, Frey JU (2003) Behavioral reinforcement of long-term potentiation in rat dentate gyrus in vivo is protein synthesis-dependent. Neurosci Lett 351: 56-58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
