Estradiol alters only GAD67 mRNA levels in ischemic rat brain with no consequent effects on GABA
- PMID: 16094313
- PMCID: PMC1410818
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600211
Estradiol alters only GAD67 mRNA levels in ischemic rat brain with no consequent effects on GABA
Abstract
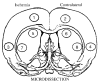
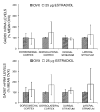
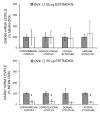
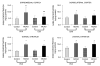
The present study tested the hypothesis that estradiol reduces tissue infarction after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in estradiol-deficient females by augmenting glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) expression and thus activity, leading to increases in gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA) tissue levels. Glutamic acid decarboxylase is the principal enzyme for GABA synthesis and has two isoforms, GAD65 and GAD67, which differ in size and cellular distribution. Rats were ovariectomized 7 to 8 days before receiving no hormone, placebo, or 25 microg estradiol via subcutaneous implant 7 to 10 days before harvesting tissue in either ischemic cohorts after 2 h of MCAO (end-ischemia) or in nonischemic cohorts. Selected cortical and striatal regions were microdissected from harvested brains. GAD65/67 mRNA levels were determined by microlysate ribonuclease protection assay. End-ischemic GABA concentrations were determined by HPLC. Steroid treatment selectively decreased ischemic cortical GAD67 mRNA levels. In most brain regions evaluated, regional GABA concentrations increased with ischemia regardless of treatment. Estradiol blocked MCAO-induced increases in GABA concentration only in dorsomedial cortex. These data suggest that estradiol repletion in ischemic rat brain selectively decreases GAD67 mRNA levels but does not alter steady-state GABA concentrations. It may be that estradiol under ischemic conditions is attenuating GABA metabolism rather than enhancing synthesis or is augmenting other aspects of GABAergic transmission such as GABA transporters and receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estrogen and ovariectomy regulate mRNA and protein of glutamic acid decarboxylases and cation-chloride cotransporters in the adult rat hippocampus.Neuroendocrinology. 2004;80(5):308-23. doi: 10.1159/000083657. Epub 2005 Jan 26. Neuroendocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15677881
-
Estrogen modulation of mRNA levels for the two forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in female rat brain.J Comp Neurol. 1995 Oct 2;360(4):685-97. doi: 10.1002/cne.903600412. J Comp Neurol. 1995. PMID: 8801259
-
GAD67 and GAD65 mRNA and protein expression in cerebrocortical regions of elderly patients with schizophrenia.J Neurosci Res. 2004 May 15;76(4):581-92. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20122. J Neurosci Res. 2004. PMID: 15114630
-
Dopaminergic regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA expression and GABA release in the striatum: a review.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1993 Nov;17(6):887-903. doi: 10.1016/0278-5846(93)90018-n. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1993. PMID: 8278600 Review.
-
Regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in the brain.J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):395-407. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03165.x. J Neurochem. 1993. PMID: 8419527 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex steroids effects on the content of GAD, TH, GABA(A), and glutamate receptors in the olfactory bulb of the male rat.Neurochem Res. 2008 Aug;33(8):1568-73. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9665-1. Epub 2008 Mar 25. Neurochem Res. 2008. PMID: 18363096
-
Treatments for seizures in catamenial (menstrual-related) epilepsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 14;10(10):CD013225. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013225.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 16;9:CD013225. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013225.pub3. PMID: 31608992 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
-
Evaluating the Cognitive Impacts of Drospirenone, a Spironolactone-Derived Progestin, Independently and in Combination With Ethinyl Estradiol in Ovariectomized Adult Rats.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 25;16:885321. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.885321. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35692432 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal omega-3 sex-selectively mitigates neuropsychiatric impacts of prenatal THC in the cortico-striatal-hippocampal circuit.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jul 28. doi: 10.1038/s41380-025-03113-x. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40721894
-
Neural Mechanisms Mediating Sex Differences in Motivation for Reward: Cognitive Bias, Food, Gambling, and Drugs of Abuse.J Neurosci. 2022 Nov 9;42(45):8477-8487. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1378-22.2022. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36351834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkayed NJ, Harukuni I, Kimes AS, London ED, Traystman RJ, Hurn PD. Gender-linked brain injury in experimental stroke. Stroke. 1998;29:159–66. - PubMed
-
- Alkayed NJ, Murphy SJ, Traystman RJ, Hurn PD. Neuroprotective effects of female gonadal steroids in reproductively senescent female rats. Stroke. 2000;31:161–8. - PubMed
-
- Bhardwaj A, Alkayed NJ, Kirsch JR, Hurn PD. Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2003;5:160–7. - PubMed
-
- Beneveniste H, Drejer J, Schousboe A, Diemer NH. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischaemia: monitoring by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1984;43:1369–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS20020/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000163/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS033668/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NR03521/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- AA11415/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- RR00163/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS07375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NR003521/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- NS33668/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS020020/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 RR000163/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HD21351/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS007375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

