Expression and alteration of insulin-like growth factor II-messenger RNA in hepatoma tissues and peripheral blood of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 16094705
- PMCID: PMC4615406
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4655
Expression and alteration of insulin-like growth factor II-messenger RNA in hepatoma tissues and peripheral blood of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the clinical values of serum free insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) levels and IGF-II mRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and peripheral blood for diagnosis of HCC and monitoring of extrahepatic metastasis.
Methods: Total RNAs were extracted from HCC tissues or peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with HCC, liver diseases devoid of cancer, non-hepatic tumors, and healthy controls, respectively. IGF-II cDNAs were synthesized through random primers and reverse-transcriptase, amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and confirmed by DNA sequencing analysis. Serum free IGF-II levels in patients with different liver diseases were analyzed by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
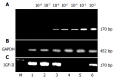
Results: The amplified fragments of IGF-II mRNA by RT-PCR were identical to originally designed ones with a size of 170 bp and confirmed by sequencing analysis. The dilution experiments revealed that the lowest sensitivity of our system was 2 ng/L of total RNA. The positive frequencies of IGF-II mRNA were 100% in HCC tissues, 53.3% in para-cancerous tissues, and 0% in non-cancerous tissues, respectively. The serum free IGF-II levels were significantly higher in HCC than those in chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis. The positive frequency of circulating IGF-II mRNA was 34.2% in HCC, no amplified fragment was found in other liver diseases, extrahepatic tumors, and normal controls, respectively. The circulating IGF-II mRNA correlated with the stage of HCC, and its positive rate was 100% in HCC with extrahepatic metastasis and 35.5% in HCC with AFP-negative. No significant correlation was found between tumor sizes and circulating IGF-II mRNA fragment.
Conclusion: The abnormal expressions of free IGF-II and IGF-II mRNA are useful tumor markers for HCC diagnosis, differentiation of extrahepatic metastasis and monitoring postoperative recurrence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characteristics of hepatic igf-ii expression and monitored levels of circulating igf-ii mRNA in metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Clin Pathol. 2010 Nov;134(5):799-806. doi: 10.1309/AJCPTFDSE2V3LCZP. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20959664
-
[Correlation between epigenetic alterations in the insulin growth factor-II gene and hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2012 Aug;20(8):593-7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2012.08.011. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23207153 Chinese.
-
[Abnormal expression of insulin-like growth factor-II and intervening of its mRNA transcription in the promotion of HepG2 cell apoptosis].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Mar 26;93(12):892-6. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23863671 Chinese.
-
Specific molecular markers in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007 Jun;6(3):241-7. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007. PMID: 17548245 Review.
-
Circulating specific biomarkers in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and its metastasis monitoring.Tumour Biol. 2014 Jan;35(1):9-20. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-1141-0. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24006223 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential roles of insulin-like growth factor receptor- and insulin receptor-mediated signaling in the phenotypes of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Neoplasia. 2009 Sep;11(9):835-45. doi: 10.1593/neo.09476. Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 19724677 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic alteration of telomerase expression and its diagnostic significance in liver or peripheral blood for hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug 21;12(31):4966-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i31.4966. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16937491 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivation of the insulin-like growth factor-II signaling pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar 21;14(11):1690-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1690. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18350600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathway of insulin-like growth factor-II as a target of molecular therapy for hepatoblastoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Oct 28;12(40):6531-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i40.6531. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17072986 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Metal Pollution and Gene Expression of Insulin-like Growth Factor II.J Health Pollut. 2018 Jun 11;8(18):180608. doi: 10.5696/2156-9614-8.18.180608. eCollection 2018 Jun. J Health Pollut. 2018. PMID: 30524857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peto J. Cancer epidemiology in the last century and the next decade. Nature. 2001;411:390–395. - PubMed
-
- Yao DF, Horie C, Horie T, Shimizu I, Meng XY, Ito S. Virological features of hepatitis C virus infection in patients with liver diseases in the inshore area of the Yangtze River. Tokushima J Exp Med. 1994;41:49–56. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu I, Yao DF, Horie C, Yasuda M, Shiba M, Horie T, Nishikado T, Meng XY, Ito S. Mutations in a hydrophilic part of the core gene of hepatitis C virus in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in China. J Gastroenterol. 1997;32:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Yao D, Jiang D, Huang Z, Lu J, Tao Q, Yu Z, Meng X. Abnormal expression of hepatoma specific gamma-glutamyl transferase and alteration of gamma-glutamyl transferase gene methylation status in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2000;88:761–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

