Biological impacts of "hot-spot" mutations of hepatitis B virus X proteins are genotype B and C differentiated
- PMID: 16094714
- PMCID: PMC4615415
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4703
Biological impacts of "hot-spot" mutations of hepatitis B virus X proteins are genotype B and C differentiated
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the biological impacts of "hot-spot" mutations on genotype B and C HBV X proteins (HBx).
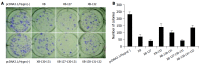
Methods: Five types of "hot-spot" mutations of genotype B or C HBV X genes, which sequentially lead to the amino acid substitutions of HBx as I127T, F132Y, K130M+V131I, I127T+K130M+V131I, or K130M+V131I+F132Y, respectively, were generated by means of site-directed mutagenesis. To evaluate the anti-proliferative effects, HBx or related mutants' expression vectors were transfected separately to the Chang cells by lipofectamine, and the cells were cultured in hygromycin selective medium for 14 d, drug-resistant colonies were fixed with cold methanol, stained with Giemsa dyes and scored (increase of the colonies indicated the reduction of the anti-proliferation activity, and vice versa). Different types of HBx expression vectors were co-transfected separately with the reporter plasmid pCMVbeta to Chang cells, which were lysed 48 h post-transfection and the intra-cellular beta-galactosidase activities were monitored (increase of the beta-galactosidase activities indicated the reduction of the transactivation activity, and vice versa). All data obtained were calculated by paired-samples t-test.
Results: As compared to standard genotype B HBx, mutants of I127T and I127T+K130M+V131I showed higher transactivation and anti-proliferative activities, while the mutants of F132Y, K130M+V131I, and K130M+V131I+F132Y showed lower activities. As compared to standard genotype C HBx, I127T mutant showed higher transactivation activity, while the other four types of mutants showed no differences. With regard to anti-proliferative activity, compared to standard genotype C HBx, F132Y and K130M+ V131I mutants showed lower activities, and K130M+V131I +F132Y mutant, on the other hand, showed higher activity, while the mutants of I127T and I127T+K130M+V131I showed no differences.
Conclusion: "Hot-spot" mutations affect the anti-proliferation and transactivation activities of genotype B and/or C HBx, and the biological impacts of most "hot-spot" mutations on HBx are genotype B and C differentiated.
Figures


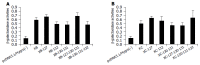
Similar articles
-
HBx-K130M/V131I Promotes Liver Cancer in Transgenic Mice via AKT/FOXO1 Signaling Pathway and Arachidonic Acid Metabolism.Mol Cancer Res. 2019 Jul;17(7):1582-1593. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-1127. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Mol Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30975706 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) X gene mutations and their association with liver disease progression in HBV-infected patients.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 6;8(62):105115-105125. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22428. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285238 Free PMC article.
-
Core promoter mutation of nucleotides A1762T and G1764A of hepatitis B virus increases core promoter transactivation by hepatocyte nuclear factor 1.J Microbiol. 2022 Oct;60(10):1039-1047. doi: 10.1007/s12275-022-1675-1. Epub 2022 Sep 27. J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36167927
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein: The X factor in chronic hepatitis B virus disease progression.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2019 Jul-Sep;37(3):387-392. doi: 10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_19_421. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 32003338
-
Review: hepatitis B virus X-gene product: a promiscuous transcriptional activator.J Med Virol. 1992 Feb;36(2):101-17. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890360207. J Med Virol. 1992. PMID: 1583465 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of hepatitis B virus X gene in HIV-positive South Africans.Virus Genes. 2018 Apr;54(2):190-198. doi: 10.1007/s11262-018-1536-5. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Virus Genes. 2018. PMID: 29411271
-
Association between host TNF-α, TGF-β1, p53 polymorphisms, HBV X gene mutation, HBV viral load and the progression of HBV-associated chronic liver disease in Indonesian patients.Biomed Rep. 2019 Oct;11(4):145-153. doi: 10.3892/br.2019.1239. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Biomed Rep. 2019. PMID: 31565220 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome analysis of hepatitis B virus before and during long-term therapy in chronic infected patients: Molecular characterization, impact on treatment and liver disease progression.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 17;13:1020147. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1020147. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36325017 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Hepatitis B Virus X Gene Mutations and Clinical Status in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection.Gut Liver. 2011 Mar;5(1):70-6. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2011.5.1.70. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Gut Liver. 2011. PMID: 21461076 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between HBx Variations and Development of Severe Liver Disease Among Indonesian Patients.Kobe J Med Sci. 2019 Jun 17;65(1):E28-E35. Kobe J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31341154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arauz-Ruiz P, Norder H, Robertson BH, Magnius LO. Genotype H: a new Amerindian genotype of hepatitis B virus revealed in Central America. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:2059–2073. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

