Lipid composition influences the shape of human low density lipoprotein in vitreous ice
- PMID: 16094859
- PMCID: PMC1249495
- DOI: 10.1007/s11745-005-1409-x
Lipid composition influences the shape of human low density lipoprotein in vitreous ice
Abstract
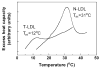
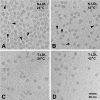
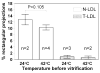
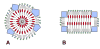
Earlier cryo-electron microscopic studies have indicated that the normal low density lipoprotein (N-LDL) has a discoid shape when its core is in the liquid-crystalline state. In the present study, we investigated whether the shape of LDL depends on the physical state and/or the lipid composition of the lipoprotein core. Using a custom-built freezing device, we vitrified NLDL samples from either above or below the phase-transition temperature of the core (42 and 24 degrees C, respectively). Cryo-electron microscopy revealed no differences between these samples and indicated a discoid shape of the N-LDL particle. In contrast, TG-enriched LDL (T-LDL) did not have discoid features and appeared to be quasi-spherical in preparations that were vitrified from either 42 or 24 degrees C. These results suggest that the shape of NLDL is discoid, regardless of the physical state of its core, whereas T-LDL is more spherical. Aspects that may influence the shape of LDL are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Hevonoja T, Pentikäinen MO, Hyvönen MT, Kovanen PT, Ala-Korpela M. Structure of Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Particles: Basis for Understanding Molecular Changes in Modified LDL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1488:189–210. - PubMed
-
- Segrest JP, Jones MK, De Loof H, Dashti N. Structure of Apolipoprotein B-100 in Low Density Lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 2001;42:1346–1367. - PubMed
-
- Borén J, Ekström U, Ågren B, Nilsson-Ehle P, Innerarity TL. The Molecular Mechanism for the Genetic Disorder Familial Defective Apolipoprotein B100. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:9214–9218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

