Nogo-B is a new physiological substrate for MAPKAP-K2
- PMID: 16095439
- PMCID: PMC1276943
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050935
Nogo-B is a new physiological substrate for MAPKAP-K2
Abstract
The neurite outgrowth inhibitor protein Nogo is one of 300 proteins that contain a reticulon homology domain, which is responsible for their association with the endoplasmic reticulum. Here we have found that the Nogo-B spliceform becomes phosphorylated at Ser107 in response to lipopolysaccharide in RAW264 macrophages or anisomycin in HeLa cells. The phosphorylation is prevented by SB 203580, an inhibitor of SAPK2a (stress-activated protein kinase 2a)/p38a and SAPK2b/p38b, and does not occur in embryonic fibroblasts generated from SAPK2a/p38a-deficient mice. Nogo-B is phosphorylated at Ser107 in vitro by MAPKAP-K2 [MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase)-activated protein kinase-2] or MAPKAP-K3, but not by other protein kinases that are known to be activated by SAPK2a/p38a. The anisomycin-induced phosphorylation of Ser107 in HeLa cells can be prevented by 'knockdown' of MAPKAP-K2 using siRNA (small interfering RNA). Taken together, our results identify Nogo-B as a new physiological substrate of MAPKAP-K2.
Figures
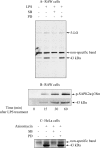


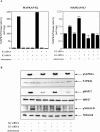
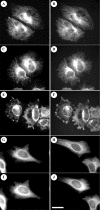
References
-
- Chen M. S., Huber A. B., van der Haar M. E., Frank M., Schnell L., Spillmann A. A., Christ F., Schwab M. E. Nogo-A is a myelin-associated neurite outgrowth inhibitor and an antigen for monoclonal antibody IN-1. Nature (London) 2000;403:434–439. - PubMed
-
- Fournier A. E., Strittmatter S. M. Repulsive factors and axon regeneration in the CNS. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001;11:89–94. - PubMed
-
- McKerracher L., Winton M. J. Nogo on the go. Neuron. 2002;36:345–348. - PubMed
-
- Spillmann A. A., Bandtlow C. E., Lottspeich F., Keller F., Schwab M. E. Identification and characterization of a bovine neurite growth inhibitor (bNI-220) J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:19283–19293. - PubMed
-
- Kim J. E., Li S., GrandPre T., Qiu D., Strittmatter S. M. Axon regeneration in young adult mice lacking Nogo-A/B. Neuron. 2003;38:187–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

