Escaping the nuclear confines: signal-dependent pre-mRNA splicing in anucleate platelets
- PMID: 16096058
- PMCID: PMC4401993
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.015
Escaping the nuclear confines: signal-dependent pre-mRNA splicing in anucleate platelets
Abstract
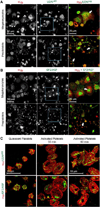
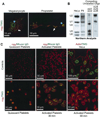
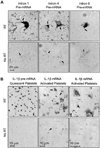
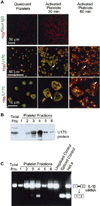
Platelets are specialized hemostatic cells that circulate in the blood as anucleate cytoplasts. We report that platelets unexpectedly possess a functional spliceosome, a complex that processes pre-mRNAs in the nuclei of other cell types. Spliceosome components are present in the cytoplasm of human megakaryocytes and in proplatelets that extend from megakaryocytes. Primary human platelets also contain essential spliceosome factors including small nuclear RNAs, splicing proteins, and endogenous pre-mRNAs. In response to integrin engagement and surface receptor activation, platelets precisely excise introns from interleukin-1beta pre-mRNA, yielding a mature message that is translated into protein. Signal-dependent splicing is a novel function of platelets that demonstrates remarkable specialization in the regulatory repertoire of this anucleate cell. While this mechanism may be unique to platelets, it also suggests previously unrecognized diversity regarding the functional roles of the spliceosome in eukaryotic cells.
Figures


Comment in
-
Splicing misplaced.Cell. 2005 Aug 12;122(3):317-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.016. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16096050 Review.
References
-
- Albertine KH, Jones GP, Starcher BC, Bohnsack JF, Davis PL, Cho SC, Carlton DP, Bland RD. Chronic lung injury in preterm lambs. Disordered respiratory tract development. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999;159:945–958. - PubMed
-
- Bahou WF, Gnatenko DV. Platelet transcriptome: the application of microarray analysis to platelets. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2004;30:473–484. - PubMed
-
- Black DL. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003;72:291–336. - PubMed
-
- Brogren H, Karlsson L, Andersson M, Wang L, Erlinge D, Jern S. Platelets synthesize large amounts of active plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Blood. 2004;104:3943–3948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL062875/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL066277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL-62875/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL044525/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD054599/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HL-66277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075507/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL044525/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL044513/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-44525/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-44513/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-75507/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

