Rpe65 is the retinoid isomerase in bovine retinal pigment epithelium
- PMID: 16096063
- PMCID: PMC2748856
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.042
Rpe65 is the retinoid isomerase in bovine retinal pigment epithelium
Abstract
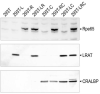
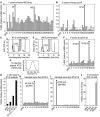
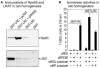
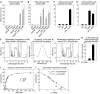
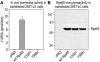
The first event in light perception is absorption of a photon by an opsin pigment, which induces isomerization of its 11-cis-retinaldehyde chromophore. Restoration of light sensitivity to the bleached opsin requires chemical regeneration of 11-cis-retinaldehyde through an enzymatic pathway called the visual cycle. The isomerase, which converts an all-trans-retinyl ester to 11-cis-retinol, has never been identified. Here, we performed an unbiased cDNA expression screen to identify this isomerase. We discovered that the isomerase is a previously characterized protein called Rpe65. We confirmed our identification of the isomerase by demonstrating catalytic activity in mammalian and insect cells that express Rpe65. Mutations in the human RPE65 gene cause a blinding disease of infancy called Leber congenital amaurosis. Rpe65 with the Leber-associated C330Y and Y368H substitutions had no isomerase activity. Identification of Rpe65 as the isomerase explains the phenotypes in rpe65-/- knockout mice and in humans with Leber congenital amaurosis.
Figures
References
-
- Arshavsky VY, Lamb TD, Pugh EN. G proteins and phototransduction. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2002;64:153–187. - PubMed
-
- Bavik CO, Eriksson U, Allen RA, Peterson PA. Identification and partial characterization of a retinal pigment epithelial membrane receptor for plasma retinol-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:14978–14985. - PubMed
-
- Bavik CO, Busch C, Eriksson U. Characterization of a plasma retinol-binding protein membrane receptor expressed in the retinal pigment epithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 1992;267:23035–23042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

