Expression of Jak3, STAT1, STAT4, and STAT6 in inflammatory arthritis: unique Jak3 and STAT4 expression in dendritic cells in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 16096332
- PMCID: PMC1798020
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2005.037929
Expression of Jak3, STAT1, STAT4, and STAT6 in inflammatory arthritis: unique Jak3 and STAT4 expression in dendritic cells in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Modulation of Jak-STAT signalling may provide an effective therapeutic strategy in inflammatory arthritis.
Objective: To document Jak-STAT expression in a cohort of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthritis (SpA), and osteoarthritis (OA) and compare these subsets with normal synovial tissue.
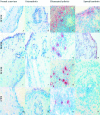
Methods: Synovial tissue biopsy specimens from patients with RA, OA, and SpA and histologically normal tissue (n = 10 in each arthritis group) were examined for the presence of Jak3, STAT1, STAT4, and STAT6 expression using immunohistochemistry. Phenotyping was performed using immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. Clinical and serological characteristics of patients with RA expressing Jak3-STAT4 were assessed.
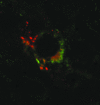
Results: STAT1, STAT4, and Jak3 protein expression was generally increased in inflammatory arthritis. In contrast, STAT6 expression was relatively heterogeneous. A subpopulation of CD1a positive dendritic cells unique to seropositive patients with RA was detected. These cells showed intense protein expression for Jak3, STAT4, and STAT6.
Conclusion: CD1a positive dendritic cells intensely express Jak3, STAT4, and STAT6 in seropositive RA tissue and may be an alternative marker for dendritic cells in their early stages of activation as well as providing a tool for identifying RA at the level of the synovium. Jak3 inhibition may be a potential therapeutic target to prevent dendritic cell maturation in RA. STAT1 expression is increased in inflammatory arthritis, suggesting that its pro-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects cannot effectively counteract inflammation. STAT6 expression is heterogeneous in synovium, suggesting a possible homoeostatic role in addition to any anti-inflammatory effects.
References
-
- Firestein G. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003423356–361. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello C A, Moldawer L L.Proinflammatory and anti‐inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. A primer for clinicians. Amgen 2002
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous