Role of aspartate 298 in mouse 5-HT3A receptor gating and modulation by extracellular Ca2+
- PMID: 16096341
- PMCID: PMC1474733
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.092866
Role of aspartate 298 in mouse 5-HT3A receptor gating and modulation by extracellular Ca2+
Abstract
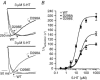
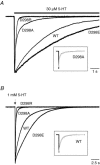
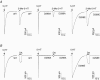
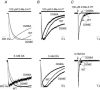
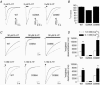
The TM2-TM3 extracellular loop is critical for activation of the Cys-loop family of ligand-gated ion channels. The contribution of aspartate 298 (D298), an amino acid that links the transmembrane domain 2 (TM2) to the TM2-TM3 loop, in mouse 5-hydroxytryptamine(3A) (5-HT(3A)) receptor function was probed with site-directed mutagenesis in the present study. This negatively charged residue was replaced with an alanine to neutralize the charge, with a glutamate to conserve the charge, or with an arginine to reverse the charge. Human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK 293) cells transfected with the wild-type and mutant receptors were studied by combining whole-cell patch-clamp recording with fast agonist application. The D-->A or D-->R mutations resulted in a receptor with reduced 5-HT potency, and accelerated kinetics of desensitization and deactivation. In addition, the efficacy of partial agonists was reduced by the D-->A mutation. The D-->E mutation produced a receptor with properties similar to those of the wild-type receptor. In addition, the potential role of this residue in modulation of the receptor by extracellular calcium ([Ca(2)(+)](o)) was investigated. Increasing [Ca(2)(+)](o) inhibited 5-HT-activated currents and altered receptor kinetics in a similar manner in the wild-type and D298E receptors, and this alteration was eliminated by the D-->A and D-->R mutations. Our data suggest that the charge at D298 participates in transitions between functional states of the 5-HT(3A) receptor, and provide evidence that the charge of the side-chain at residue D298 contributes to channel gating kinetics and is crucial for Ca(2)(+) modulation.
Figures
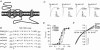


References
-
- Absalom NL, Lewis TM, Kaplan W, Pierce KD, Schofield PR. Role of charged residues in coupling ligand binding and channel activation in the extracellular domain of the glycine receptor. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:50151–50157. - PubMed
-
- Bera AK, Chatav M, Akabas MH. GABAA receptor M2–M3 loop secondary structure and changes in accessibility during channel gating. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:43002–43010. - PubMed
-
- Bouzat C, Gumilar F, Spitzmaul G, Wang HL, Rayes D, Hansen SB, Taylor P, Sine SM. Coupling of agonist binding to channel gating in an ACh-binding protein linked to an ion channel. Nature. 2004;430:896–900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

