Prion generation in vitro: amyloid of Ure2p is infectious
- PMID: 16096644
- PMCID: PMC1201353
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600772
Prion generation in vitro: amyloid of Ure2p is infectious
Abstract
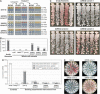
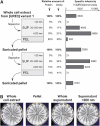
[URE3] is a prion (infectious protein) of the Ure2 protein of yeast. In vitro, Ure2p can form amyloid filaments, but direct evidence that these filaments constitute the infectious form is still missing. Here we demonstrate that recombinant Ure2p converted into amyloid can infect yeast cells lacking the prion. Infection produced a variety of [URE3] variants. Extracts of [URE3] strains, as well as amyloid of Ure2p formed in an extract-primed reaction could transmit to uninfected cells the [URE3] variant present in the cells from which the extracts were made. Infectivity and determinant of [URE3] variants resided within the N-terminal 65 amino acids of Ure2p. Notably, we could show that amyloid filaments of recombinant Ure2p are nearly as infectious per mass of Ure2p as extracts of [URE3] strains. Sizing experiments indicated that infectious particles in vitro and in vivo were >20 nm in diameter, suggesting that they were amyloid filaments and not smaller oligomeric structures. Our data indicate that there is no substantial difference between filaments formed in vivo and in vitro.
Figures




References
-
- Aigle M, Lacroute F (1975) Genetical aspects of [URE3], a non-Mendelian, cytoplasmically inherited mutation in yeast. Mol Gen Genet 136: 327–335 - PubMed
-
- Amberg D, Burke DJ, Strathern JN (2005) Methods in Yeast Genetics. Woodbury, NY, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
-
- Baxa U, Cheng N, Winkler DC, Chiu TK, Davies DR, Sharma D, Inouye H, Kirschner DA, Wickner RB, Steven AC (2005) Filaments of the Ure2p prion protein have a cross-beta core structure. J Struct Biol 150: 170–179 - PubMed
-
- Baxa U, Taylor KL, Wall JS, Simon MN, Cheng N, Wickner RB, Steven A (2003) Architecture of Ure2p prion filaments: the N-terminal domain forms a central core fiber. J Biol Chem 278: 43717–43727 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

