Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in gastric cancer and its relation to liver metastasis and long-term prognosis
- PMID: 16097070
- PMCID: PMC4398748
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i31.4911
Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in gastric cancer and its relation to liver metastasis and long-term prognosis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in gastric cancer and its relation with the liver metastasis and prognosis.
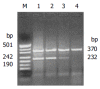
Methods: Expression of COX-2 mRNA and protein was examined in gastric cancer and its paired substantial normal tissue by semi-quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. The relation between COX-2 expression and prognosis was investigated in 195 cases.
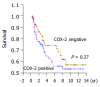
Results: The expression of COX-2 mRNA in gastric cancer tissue was significantly higher than that in normal tissue in 47 cases (w = 792, P<0.01). The COX-2 mRNA in pT3-4 tissue expressed higher than that in pT1-2 tissue (w = 204, P<0.05). The positive expression rate of COX-2 protein was 57.9% (113/195). The COX-2 expression was significantly related to histological type, lymphnode metastasis, venous invasion and liver metastasis (P<0.05). No relation was found between COX-2 expression and invasion depth, peritoneal metastasis and International Union against Cancer TNM stage. The multiple regression analysis showed that the COX-2 expression and venous invasion were obviously associated with liver metastasis (P<0.05). However, there was no significant correlation between COX-2 immunoreactivity and prognosis.
Conclusion: COX-2 may play an important role in the development of gastric cancer, and the over-expression of COX-2 protein may be a high risk factor for liver metastasis.
Figures
References
-
- Farrow DC, Vaughan TL, Hansten PD, Stanford JL, Risch HA, Gammon MD, Chow WH, Dubrow R, Ahsan H, Mayne ST, et al. Use of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of esophageal and gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1998;7:97–102. - PubMed
-
- García-Rodríguez LA, Huerta-Alvarez C. Reduced risk of colorectal cancer among long-term users of aspirin and nonaspirin nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Epidemiology. 2001;12:88–93. - PubMed
-
- Morgan G. Beneficial effects of NSAIDs in the gastrointestinal tract. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;11:393–400. - PubMed
-
- Funkhouser EM, Sharp GB. Aspirin and reduced risk of esophageal carcinoma. Cancer. 1995;76:1116–1119. - PubMed
-
- Taketo MM. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in tumorigenesis (Part II) J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:1609–1620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials