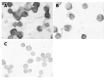
Expression of heparanase mRNA in anti-sense oligonucleotide-transfected human esophageal cancer EC9706 cells
- PMID: 16097072
- PMCID: PMC4398750
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i31.4916
Expression of heparanase mRNA in anti-sense oligonucleotide-transfected human esophageal cancer EC9706 cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of anti-sense oligonucleotides (ASODNs) on mRNA expression of heparanase in human esophageal cancer EC9706 cells.
Methods: One non-sense oligonucleotide (N-ODN) and five ASODNs against different heparanase mRNA sites were transfected into EC9706 cells, then the expression of heparanase mRNA in EC9706 cells was studied by in situ hybridization.
Results: The expression of heparanase mRNA could be inhibited by ASODNs. There was no significant difference among five ASODNs (P>0.05), but there was a significant difference between ASODNs and N-ODN or non-transfected group (ASODN1: 2.25+/-0.25, ASODN2: 2.21+/-0.23, ASODN3: 2.23+/-0.23, ASODN4: 2.25+/-0.24 vs N-ODN: 3.47+/-2.80 or non- transfected group: 3.51+/-2.93 respectively, P<0.05).
Conclusion: The expression of heparanase mRNA in EC9706 cells can be inhibited by ASODNs in vivo, and heparanase ASODNs can inhibit metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma or other tumors by inhibiting the expression of heparanase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Inhibitory effect of silencing heparanase expression with antisense oligodeoxynucleotide on invasive capability of human esophageal squamous cancer cell line TE-13].Ai Zheng. 2005 Dec;24(12):1431-5. Ai Zheng. 2005. PMID: 16351787 Chinese.
-
Survivin antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits growth of gastric cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Apr 15;10(8):1121-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1121. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15069710 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibitory effects of nanosize delivery system for antisense oligonucleotide of hTERT on EC9706 cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):329-34. doi: 10.4161/cbt.6.3.3662. Epub 2007 Mar 4. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17438368
-
The role of heparanase in gastrointestinal cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2005 Jul;14(1):3-8. Oncol Rep. 2005. PMID: 15944760 Review.
-
Mammalian heparanase as mediator of tumor metastasis and angiogenesis.Isr Med Assoc J. 2000 Jul;2 Suppl:37-45. Isr Med Assoc J. 2000. PMID: 10909416 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation of a human gallbladder cancer cell clone with high invasive phenotype in vitro and metastatic potential in orthotopic model and inhibition of its invasiveness by heparanase antisense oligodeoxynucleotides.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2007;24(1):25-38. doi: 10.1007/s10585-006-9053-7. Epub 2007 Jan 27. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2007. PMID: 17260103
References
-
- Vlodavsky I, Friedmann Y, Elkin M, Aingorn H, Atzmon R, Ishai-Michaeli R, Bitan M, Pappo O, Peretz T, Michal I, et al. Mammalian heparanase: gene cloning, expression and function in tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 1999;5:793–802. - PubMed
-
- Nakajima M, Irimura T, Di Ferrante D, Di Ferrante N, Nicolson GL. Heparan sulfate degradation: relation to tumor invasive and metastatic properties of mouse B16 melanoma sublines. Science. 1983;220:611–613. - PubMed
-
- Chen KS, Zheng NG, Wu JL, Ding Y, Wang YL. Effects of 8-Br-cAMP on growth related gene expression of human esophageal cancer cell line Eca-109. Jiepou Xuebao. 1999;30:227–229.
-
- Vaday GG, Lider O. Extracellular matrix moieties, cytokines, and enzymes: dynamic effects on immune cell behavior and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;67:149–159. - PubMed
-
- Graham LD, Underwood PA. Comparison of the heparanase enzymes from mouse melanoma cells, mouse macrophages, and human platelets. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1996;39:563–571. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources