Role of MKK3 and p38 MAPK in cytokine-induced death of insulin-producing cells
- PMID: 16097952
- PMCID: PMC1383671
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050814
Role of MKK3 and p38 MAPK in cytokine-induced death of insulin-producing cells
Abstract
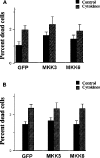
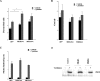
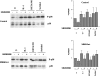
The aim of the present investigation was to elucidate further the importance of p38 MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) in nitric oxide- and cytokine-induced beta-cell death. For this purpose, isolated human islets were treated with d-siRNA (diced small interfering RNA) and then exposed to the nitric oxide donor DETA/NONOate [2,2'-(hydroxynitrosohydrazono)bis-ethanamine]. We observed that cells treated with p38alpha-specific d-siRNA, but not with d-siRNA targeting GL3 (a firefly luciferase siRNA plasmid) or PKCdelta (protein kinase Cdelta), were protected against nitric oxide-induced death. This was paralleled by an increased level of Bcl-XL (B-cell leukaemia/lymphoma-X long). For an in-depth study of the mechanisms of p38 activation, MKK3 (MAPK kinase 3), MKK6 and their dominant-negative mutants were overexpressed in insulin-producing RIN-5AH cells. In transient transfections, MKK3 overexpression resulted in increased p38 phosphorylation, whereas in stable MKK3-overexpressing RIN-5AH clones, the protein levels of p38 and JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase) were decreased, resulting in unaffected phospho-p38 levels. In addition, a long-term MKK3 overexpression did not affect cell death rates in response to the cytokines interleukin-1beta and interferon-gamma, whereas a short-term MKK3 expression resulted in increased cytokine-induced RIN-5AH cell death. The MKK3-potentiating effect on cytokine-induced cell death was abolished by a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, and MKK3-stimulated p38 phosphorylation was enhanced by inhibitors of phosphatases. Finally, as the dominant-negative mutant of MKK3 did not affect cytokine-induced p38 phosphorylation, and as wild-type MKK3 did not influence p38 autophosphorylation, it may be that p38 is activated by MKK3/6-independent pathways in response to cytokines and nitric oxide. In addition, it is likely that a long-term increase in p38 activity is counteracted by both a decreased expression of the p38, JNK and p42 genes as well as an increased dephosphorylation of p38.
Figures
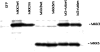

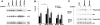
Similar articles
-
Effects of sodium ferulate on amyloid-beta-induced MKK3/MKK6-p38 MAPK-Hsp27 signal pathway and apoptosis in rat hippocampus.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006 Oct;27(10):1309-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00414.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006. PMID: 17007737
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediate double-strand RNA-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in microglial cells.Neurosci Lett. 2008 Mar 15;433(3):215-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.10.052. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Neurosci Lett. 2008. PMID: 18258363
-
Transforming growth factor-beta-activated protein kinase 1-binding protein (TAB)-1alpha, but not TAB1beta, mediates cytokine-induced p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation and cell death in insulin-producing cells.Endocrinology. 2008 Jan;149(1):302-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0690. Epub 2007 Oct 11. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 17932218
-
p38 MAP kinase inhibitors: many are made, but few are chosen.Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2005 Jul;8(4):421-30. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2005. PMID: 16022178 Review.
-
Regulation of pancreatic β-cell survival by nitric oxide: clinical relevance.Islets. 2012 Mar-Apr;4(2):108-18. doi: 10.4161/isl.19822. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Islets. 2012. PMID: 22614339 Review.
Cited by
-
Exendin-4 protects murine MIN6 pancreatic β-cells from interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis via the NF-κB pathway.J Endocrinol Invest. 2013 Nov;36(10):803-11. doi: 10.3275/8938. Epub 2013 Apr 18. J Endocrinol Invest. 2013. PMID: 23609920
-
P38alpha-selective mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor for improvement of cultured human islet recovery.Pancreas. 2010 May;39(4):436-43. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181c0dd8f. Pancreas. 2010. PMID: 20084046 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TAB1 in nitric oxide-induced p38 activation in insulin-producing cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2006 Nov 25;3(2):71-6. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.3.71. Int J Biol Sci. 2006. PMID: 17205106 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK kinase kinase-1 is essential for cytokine-induced c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human pancreatic islet cells.Diabetes. 2008 Jul;57(7):1896-904. doi: 10.2337/db07-1670. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18420486 Free PMC article.
-
T cells cooperate with palmitic acid in induction of beta cell apoptosis.BMC Immunol. 2009 May 22;10:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-10-29. BMC Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19463182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bendtzen K., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Nerup J., Nielsen J. H., Dinarello C. A., Svenson M. Cytotoxicity of human pI 7 interleukin-1 for pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Science. 1986;232:1545–1547. - PubMed
-
- Eizirik D. L., Mandrup-Poulsen T. A choice of death – the signal-transduction of immune-mediated beta-cell apoptosis. Diabetologia. 2001;44:2115–2133. - PubMed
-
- Welsh N., Eizirik D. L., Bendtzen K., Sandler S. Interleukin-1 beta-induced nitric oxide production in isolated rat pancreatic islets requires gene transcription and may lead to inhibition of the Krebs cycle enzyme aconitase. Endocrinology. 1991;129:3167–3173. - PubMed
-
- Barbu A., Welsh N., Saldeen J. Cytokine-induced apoptosis and necrosis are preceded by disruption of the mitochondrial membrane potential (Deltapsi(m)) in pancreatic RINm5F cells: prevention by Bcl-2. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002;190:75–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

