Effect of structural transition of the host assembly on dynamics of an ion channel peptide: a fluorescence approach
- PMID: 16100280
- PMCID: PMC1366802
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.060798
Effect of structural transition of the host assembly on dynamics of an ion channel peptide: a fluorescence approach
Abstract
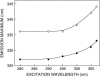
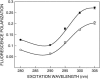
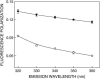
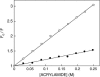
Structural transition can be induced in charged micelles by increasing the ionic strength of the medium. We have monitored the organization and dynamics of the functionally important tryptophan residues of gramicidin in spherical and rod-shaped sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles utilizing a combination of wavelength-selective fluorescence and related fluorescence approaches. Our results show that tryptophans in gramicidin, present in the single-stranded beta(6.3) conformation, experience slow solvent relaxation giving rise to red edge excitation shift in spherical and rod-shaped micelles. In addition, changes in fluorescence polarization with increasing excitation or emission wavelength reinforce that the gramicidin tryptophans are localized in motionally restricted regions of these micelles. Fluorescence quenching experiments using acrylamide as a quencher of tryptophan fluorescence show that there is reduced water penetration in rod-shaped micelles. Taken together, we show that gramicidin conformation and dynamics is sensitive to the salt-induced structural transition in charged micelles. In addition, these results demonstrate that deformation of the host assembly could modulate protein conformation and dynamics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of graded hydration on the dynamics of an ion channel peptide: a fluorescence approach.Biophys J. 2005 Feb;88(2):1070-80. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.051490. Epub 2004 Nov 12. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15542551 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of structural transition of the host assembly on dynamics of a membrane-bound tryptophan analogue.Biophys Chem. 2007 Sep;129(2-3):172-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2007.05.017. Epub 2007 Jun 6. Biophys Chem. 2007. PMID: 17590497
-
Motionally restricted tryptophan environments at the peptide-lipid interface of gramicidin channels.Biochemistry. 1994 May 3;33(17):5089-97. doi: 10.1021/bi00183a012. Biochemistry. 1994. PMID: 7513554
-
Structural transition in micelles: novel insight into microenvironmental changes in polarity and dynamics.Chem Phys Lipids. 2012 May;165(4):497-504. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2011.09.007. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Chem Phys Lipids. 2012. PMID: 21964446 Review.
-
Exploring membrane organization and dynamics by the wavelength-selective fluorescence approach.Chem Phys Lipids. 2003 Jan;122(1-2):3-17. doi: 10.1016/s0009-3084(02)00174-3. Chem Phys Lipids. 2003. PMID: 12598034 Review.
Cited by
-
Importance of indole N-H hydrogen bonding in the organization and dynamics of gramicidin channels.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1838(1 Pt B):419-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Oct 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24148157 Free PMC article.
-
Localization and dynamics of the anticarcinogenic curcumin with GM1 and other miceller assemblies.Glycoconj J. 2017 Apr;34(2):171-179. doi: 10.1007/s10719-016-9748-1. Epub 2016 Nov 19. Glycoconj J. 2017. PMID: 27866299
-
Orientation and dynamics of melittin in membranes of varying composition utilizing NBD fluorescence.Biophys J. 2007 Feb 15;92(4):1271-83. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.088690. Epub 2006 Nov 17. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17114219 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane organization and dynamics of "inner pair" and "outer pair" tryptophan residues in gramicidin channels.J Phys Chem B. 2012 Sep 13;116(36):11056-64. doi: 10.1021/jp304846f. Epub 2012 Aug 30. J Phys Chem B. 2012. PMID: 22892073 Free PMC article.
-
Role of tryptophan residues in gramicidin channel organization and function.Biophys J. 2008 Jul;95(1):166-75. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.124206. Epub 2008 Mar 13. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18339735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chattopadhyay, A., K. G. Harikumar, and S. Kalipatnapu. 2002. Solubilization of high affinity G-protein-coupled serotonin1A receptors from bovine hippocampus using pre-micellar CHAPS at low concentration. Mol. Membr. Biol. 19:211–220. - PubMed
-
- Seddon, A. M., P. Curnow, and P. J. Booth. 2004. Membrane proteins, lipids and detergents: not just a soap opera. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1666:105–117. - PubMed
-
- Tanford, C. 1978. The hydrophobic effect and the organization of living matter. Science. 200:1012–1018. - PubMed
-
- Israelachvili, J. N., S. Marcelja, and R. G. Horn. 1980. Physical principles of membrane organization. Q. Rev. Biophys. 13:121–200. - PubMed
-
- Sham, S. S., S. Shobana, L. E. Townsley, J. B. Jordan, J. Q. Fernandez, O. S. Andersen, D. V. Greathouse, and J. F. Hinton. 2003. The structure, cation binding, transport and conductance of Gly15-gramicidin A incorporated into SDS micelles and PC/PG vesicles. Biochemistry. 42:1401–1409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

