Using multiple alignments to improve seeded local alignment algorithms
- PMID: 16100379
- PMCID: PMC1185574
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki767
Using multiple alignments to improve seeded local alignment algorithms
Abstract
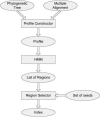
Multiple alignments among genomes are becoming increasingly prevalent. This trend motivates the development of tools for efficient homology search between a query sequence and a database of multiple alignments. In this paper, we present an algorithm that uses the information implicit in a multiple alignment to dynamically build an index that is weighted most heavily towards the promising regions of the multiple alignment. We have implemented Typhon, a local alignment tool that incorporates our indexing algorithm, which our test results show to be more sensitive than algorithms that index only a sequence. This suggests that when applied on a whole-genome scale, Typhon should provide improved homology searches in time comparable to existing algorithms.
Figures






References
-
- Waterston R.H., Lindblad-Toh K., Birney E., Rogers J., Abril J.F., Agarwal P., Agarwala R., Ainscough R., Alexandersson M., An P., et al. Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature. 2002;420:520–562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

