Effect of high dose inhaled glucocorticoids on quality of life in patients with moderate to severe asthma
- PMID: 16100448
- PMCID: PMC2782152
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.4.586
Effect of high dose inhaled glucocorticoids on quality of life in patients with moderate to severe asthma
Abstract
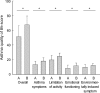
Asthma is a chronic disorder that can place considerable restrictions on the physical, emotional, and social aspects of the lives of patients. Inhaled glucocorticoids (GCs) are the most effective controller therapy. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of inhaled GCs on quality of life in patients with moderate to severe asthma. Patients completed the asthma quality of life questionnaire (AQLQ) and pulmonary function test at baseline and after 4 wks treatment of GCs. We enrolled 60 patients who had reversibility in FEV1 after 200 microgram of albuterol of 15% or more and/or positive methacholine provocation test, and initial FEV1% predicted less than 80%. All patients received inhaled GCs (fluticasone propionate 1,000 microgram/day) for 4 wks. The score of AQLQ was significantly improved following inhaled GCs (overall 51.9+/-14.3 vs. 67.5+/-12.1, p<0.05). The change from day 1 to day 28 in FEV1 following inhaled GCs was diversely ranged from -21.0% to 126.8%. The improvement of score of AQLQ was not different between at baseline and after treatment of GCs according to asthma severity and GCs responsiveness. Quality of life was improved after inhaled GCs regardless of asthma severity and GCs responsiveness in patients with moderate to severe asthma.
Figures
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. NHLBI/WHO workshop report. Bethesda, Md: National Institutes of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; 2002. NIH publication no. 02-3659. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110:S141–S219. - PubMed
-
- Blaiss MS. Outcomes analysis in asthma. JAMA. 1997;278:1874–1880. - PubMed
-
- Guyatt GH, Feeny DH, Patrick DL. Measuring health-related quality of life. Ann Intern Med. 1993;118:622–629. - PubMed
-
- Juniper EF. Quality of life in adults and children with asthma and rhinitis. Allergy. 1997;52:971–977. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ. Inhaled glucocorticoids for asthma. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:868–875. - PubMed