Neutrophils and the kallikrein-kinin system in proteinase-activated receptor 4-mediated inflammation in rodents
- PMID: 16100525
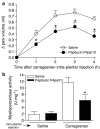
- PMCID: PMC1751199
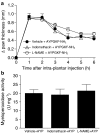
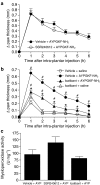
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706371
Neutrophils and the kallikrein-kinin system in proteinase-activated receptor 4-mediated inflammation in rodents
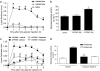
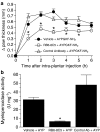
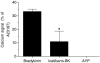
Abstract
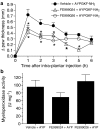
1 We evaluated a potential role for proteinase-activated receptor 4 (PAR(4)) in a rodent paw inflammation model, with a focus on two main features of inflammation: (1) oedema and (2) granulocyte recruitment. 2 A PAR(4) antagonist (Pepducin P4pal-10; palmitoyl-SGRRYGHALR-NH(2)) reduced both the oedema and granulocyte recruitment induced by a localized administration of carrageenan in the rat hind paw, pointing to a key role for PAR(4) in this inflammation model. 3 Further, intraplantar injection in the mouse hind paw of a PAR(4) agonist (AYPGKF-NH(2)), but not its standard PAR(4)-inactive peptide control (YAPGKF-NH(2)), caused an inflammatory reaction characterized by oedema (increased paw thickness) and granulocyte recruitment (increased paw myeloperoxidase activity). The PAR(4) agonist-induced effects were inhibited in mice pretreated with pepducin P4pal10. 4 These PAR(4) agonist-mediated effects were not affected by pretreatment with inhibitors of either NO production or prostaglandin release (L-NAME and indomethacin, respectively). 5 However, selective immuno-depletion of neutrophils significantly reduced PAR(4) agonist-induced oedema formation. 6 Moreover, AYPGKF-NH(2)-induced oedema was also reduced by pretreatment with either a kinin B(2) receptor antagonist (icatibant) or a tissue or plasma kallikrein inhibitor (FE999024 and FE999026, respectively), but not with a kinin B(1) receptor antagonist (SSR240612). 7 We conclude: (1) that PAR(4) plays an important role in the inflammatory response as it mediates some of the hallmarks of inflammation and (2) that PAR(4)-mediated oedema is dependent on the recruitment of neutrophils and components of the kallikrein-kinin system.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Triggering of proteinase-activated receptor 4 leads to joint pain and inflammation in mice.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Mar;60(3):728-37. doi: 10.1002/art.24300. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19248120
-
Proteinase-activated receptor-4 plays a major role in the recruitment of neutrophils induced by trypsin or carrageenan during pleurisy in mice.Pharmacology. 2012;89(5-6):275-82. doi: 10.1159/000337378. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Pharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22517275
-
Proteinase-activated receptor-4: evaluation of tethered ligand-derived peptides as probes for receptor function and as inflammatory agonists in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Oct;143(4):443-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705946. Epub 2004 Sep 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15451771 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic stroke and traumatic brain injury: the role of the kallikrein-kinin system.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Feb-Mar;101-102:65-82. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.11.004. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23274649 Review.
-
Kallikrein-kinin in infection and cancer.Immunopharmacology. 1999 Sep;43(2-3):115-28. doi: 10.1016/s0162-3109(99)00104-6. Immunopharmacology. 1999. PMID: 10596842 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Protease-Activated Receptor 4 (PAR4)-Tethered Ligand Antagonists Using Ultralarge Virtual Screening.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Mar 21;7(4):1086-1100. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00378. eCollection 2024 Apr 12. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38633591 Free PMC article.
-
Protease-activated receptor 4: a critical participator in inflammatory response.Inflammation. 2015 Apr;38(2):886-95. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9999-6. Inflammation. 2015. PMID: 25120239 Review.
-
A role for transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 in tonicity-induced neurogenic inflammation.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Mar;159(5):1161-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00590.x. Epub 2010 Feb 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20136846 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of proteinase-activated receptor 4 inhibits neutrophil recruitment in experimental inflammation in mice.Inflamm Res. 2014 Nov;63(11):935-41. doi: 10.1007/s00011-014-0767-8. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Inflamm Res. 2014. PMID: 25118784
-
Pharmacology, biodistribution, and efficacy of GPCR-based pepducins in disease models.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;683:259-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-919-2_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21053136 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ASOKANANTHAN N., GRAHAM P.T., FINK J., KNIGHT D.A., BAKKER A.J., MCWILLIAM A.S., THOMPSON P.J., STEWART G.A. Activation of protease-activated receptor (PAR)-1, PAR-2, and PAR-4 stimulates IL-6, IL-8, and prostaglandin E2 release from human respiratory epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2002;168:3577–3585. - PubMed
-
- BLAUKAT A., PIZARD A., BREIT A., WERNSTEDT C., HENC-GELAS F., MULLER-ESTERL W., DIKIC I. Determination of bradykinin B2 receptor in vivo phosphorylation sites and their role in receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:40431–40440. - PubMed
-
- BONDER C.S., AJUEBOR M.N., ZBYTNUIK L.D., KUBES P., SWAIN M.G. Essential role for neutrophil recruitment to the liver in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. J. Immunol. 2004;172:45–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

