The cellular TATA binding protein is required for rep-dependent replication of a minimal adeno-associated virus type 2 p5 element
- PMID: 16103159
- PMCID: PMC1193596
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.11082-11094.2005
The cellular TATA binding protein is required for rep-dependent replication of a minimal adeno-associated virus type 2 p5 element
Abstract
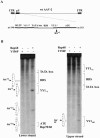
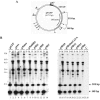
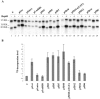
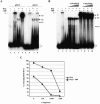
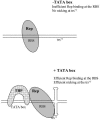
The p5 promoter region of adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV-2) is a multifunctional element involved in rep gene expression, Rep-dependent replication, and site-specific integration. We initially characterized a 350-bp p5 region by its ability to behave like a cis-acting replication element in the presence of Rep proteins and adenoviral factors. The objective of this study was to define the minimal elements within the p5 region required for Rep-dependent replication. Assays performed in transfected cells (in vivo) indicated that the minimal p5 element was composed by a 55-bp sequence (nucleotides 250 to 304 of wild-type AAV-2) containing the TATA box, the Rep binding site, the terminal resolution site present at the transcription initiation site (trs(+1)), and a downstream 17-bp region that could potentially form a hairpin structure localizing the trs(+1) at the top of the loop. Interestingly, the TATA box was absolutely required for in vivo but dispensable for in vitro, i.e., cell-free, replication. We also demonstrated that Rep binding and nicking at the trs(+1) was enhanced in the presence of the cellular TATA binding protein, and that overexpression of this cellular factor increased in vivo replication of the minimal p5 element. Together, these studies identified the minimal replication origin present within the AAV-2 p5 promoter region and demonstrated for the first time the involvement of the TATA box, in cis, and of the TATA binding protein, in trans, for Rep-dependent replication of this viral element.
Figures


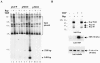

References
-
- Berns, K. I., and C. Giraud. 1996. Biology of adeno-associated virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 218:1-23. - PubMed
-
- Boyd, J. M., P. M. Loewenstein, Q.-Q. Tang, L. Yu, and M. Green. 2002. Adenovirus E1A N-terminal amino acid sequence requirements for repression of transcription in vitro and in vivo correlate with those required for E1A interference with TBP-TATA complex formation. J. Virol. 76:1461-1474. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burgess Hickman, A., D. R. Ronning, Z. N. Perez, R. M. Kotin, and F. Dyda. 2004. The nuclease domain of adeno-associated virus Rep coordinates replication initiation using two distinct DNA recognition interfaces. Mol. Cell 13:403-414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

