Adenovirus type 5 E4orf3 protein targets the Mre11 complex to cytoplasmic aggresomes
- PMID: 16103189
- PMCID: PMC1193610
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.11382-11391.2005
Adenovirus type 5 E4orf3 protein targets the Mre11 complex to cytoplasmic aggresomes
Abstract
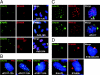
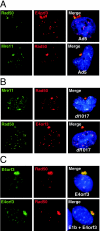
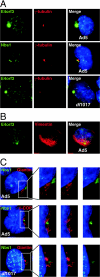
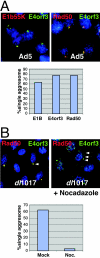
Virus infections have dramatic effects on structural and morphological characteristics of the host cell. The gene product of open reading frame 3 in the early region 4 (E4orf3) of adenovirus serotype 5 (Ad5) is involved in efficient replication and late protein synthesis. During infection with adenovirus mutants lacking the E4 region, the viral genomic DNA is joined into concatemers by cellular DNA repair factors, and this requires the Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex. Concatemer formation can be prevented by the E4orf3 protein, which causes the cellular redistribution of the Mre11 complex. Here we show that E4orf3 colocalizes with components of the Mre11 complex in nuclear tracks and also in large cytoplasmic accumulations. Rearrangement of Mre11 and Rad50 by Ad5 E4orf3 is not dependent on interactions with Nbs1 or promyelocytic leukemia protein nuclear bodies. Late in infection the cytoplasmic inclusions appear as a distinct juxtanuclear accumulation at the centrosome and this requires an intact microtubule cytoskeleton. The large cytoplasmic accumulations meet the criteria defined for aggresomes, including gamma-tubulin colocalization and formation of a surrounding vimentin cage. E4orf3 also appears to alter the solubility of the cellular Mre11 complex. These data suggest that E4orf3 can target the Mre11 complex to an aggresome and may explain how the cellular repair complex is inactivated during adenovirus infection.
Figures
References
-
- Blair Zajdel, M. E., and G. E. Blair. 1988. The intracellular distribution of the transformation-associated protein p53 in adenovirus-transformed rodent cells. Oncogene 2:579-584. - PubMed
-
- Boyer, J., K. Rohleder, and G. Ketner. 1999. Adenovirus E4 34k and E4 11k inhibit double strand break repair and are physically associated with the cellular DNA-dependent protein kinase. Virology 263:307-312. - PubMed
-
- Bridge, E., and G. Ketner. 1990. Interaction of adenoviral E4 and E1b products in late gene expression. Virology 174:345-353. - PubMed
-
- Brown, C. R., S. J. Doxsey, E. White, and W. J. Welch. 1994. Both viral (adenovirus E1B) and cellular (hsp 70, p53) components interact with centrosomes. J. Cell Physiol. 160:47-60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

