Cyclic AMP and calcium interplay as second messengers in melatonin-dependent regulation of Plasmodium falciparum cell cycle
- PMID: 16103224
- PMCID: PMC2171486
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200505117
Cyclic AMP and calcium interplay as second messengers in melatonin-dependent regulation of Plasmodium falciparum cell cycle
Abstract
The host hormone melatonin increases cytoplasmic Ca(2+) concentration and synchronizes Plasmodium cell cycle (Hotta, C.T., M.L. Gazarini, F.H. Beraldo, F.P. Varotti, C. Lopes, R.P. Markus, T. Pozzan, and C.R. Garcia. 2000. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:466-468). Here we show that in Plasmodium falciparum melatonin induces an increase in cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) activity (40 and 50%, respectively). When red blood cells infected with P. falciparum are treated with cAMP analogue adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate N6-benzoyl/PKA activator (6-Bz-cAMP) there is an alteration of the parasite cell cycle. This effect appears to depend on activation of PKA (abolished by the PKA inhibitors adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphorothioate/8 Bromo Rp isomer, PKI [cell permeable peptide], and H89). An unexpected cross talk was found to exist between the cAMP and the Ca(2+)-dependent signaling pathways. The increases in cAMP by melatonin are inhibited by blocker of phospholipase C U73122, and addition of 6-Bz-cAMP increases cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration, through PKA activation. These findings suggest that in Plasmodium a highly complex interplay exists between the Ca(2+) and cAMP signaling pathways, but also that the control of the parasite cell cycle by melatonin requires the activation of both second messenger controlled pathways.
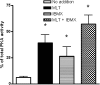
Figures





References
-
- Alleva, L.M., and K. Kirk. 2001. Calcium regulation in the intraerythrocytic malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 117:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Aravind L., L.M. Iyer, T.E. Wellems, and L.H. Miller. 2003. Plasmodium biology: genomic gleanings. Cell. 115:771–785. - PubMed
-
- Bannister, L., and G. Mitchell. 2003. The ins, outs and roundabouts of malaria. Trends Parasitol. 19:209–213. - PubMed
-
- Beraldo, F.H., and C.R. Garcia. 2005. Products of tryptophan catabolism induce a Ca2+ release and modulate the cell cycle of P. fal ciparum malaria parasites J. Pineal Res. In press. - PubMed
-
- Berridge, M.J., M.D. Bootman, and H.L. Roderick. 2003. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4:517–529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

