The protein farnesyltransferase inhibitor Tipifarnib as a new lead for the development of drugs against Chagas disease
- PMID: 16107140
- PMCID: PMC3265986
- DOI: 10.1021/jm050441z
The protein farnesyltransferase inhibitor Tipifarnib as a new lead for the development of drugs against Chagas disease
Abstract
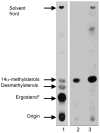
Tipifarnib (R115777), an inhibitor of human protein farnesyltransferase (PFT), is shown to be a highly potent inhibitor of Trypanosoma cruzi growth (ED(50) = 4 nM). Surprisingly, this is due to the inhibition of cytochrome P450 sterol 14-demethylase (CYP51, EC 1.14.13.70). Homology models of the T. cruzi CYP51 were used for the prediction of the binding modes of the substrate lanosterol and of Tipifarnib, providing a basis for the design of derivatives with selectivity for TcCYP51 over human PFT.
Figures

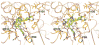
References
-
- Buckner FS, Eastman RT, Nepomuceno-Silva JL, Speelmon EC, Myler PJ, et al. Cloning, heterologous expression, and substrate specificities of protein farnesyltransferases from Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania major. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002;122:181–188. - PubMed
-
- Sebti SM, Adjei AA. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors. Sem Oncol. 2004;31:28–39. - PubMed
-
- Sali A, Blundell TL. Comparative Protein Modeling by Satisfaction of Spatial Restraints. J Mol Biol. 1993;234:779–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

