G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis induced by SARS-CoV 3b protein in transfected cells
- PMID: 16107218
- PMCID: PMC1190220
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-2-66
G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis induced by SARS-CoV 3b protein in transfected cells
Abstract
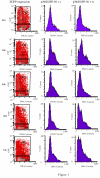
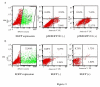
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), cause of the life-threatening atypical pneumonia, infects many organs, such as lung, liver and immune organ, and induces parenchyma cells apoptosis and necrosis. The genome of SARS-CoV, not closely related to any of the previously characterized coronavirus, encodes replicase and four major structural proteins and a number of non-structural proteins. Published studies suggest that some non-structural proteins may play important roles in the replication, virulence and pathogenesis of viruses. Among the potential SARS-CoV non-structural proteins, 3b protein (ORF4) is predicted encoding 154 amino acids, lacking significant similarities to any known proteins. Till now, there is no report about the function of 3b protein. In this study, 3b gene was linked with the EGFP tag at the C- terminus. Through cell cycle analysis, it was found that over-expression of 3b-EGFP protein in Vero, 293 and COS-7 cells could induce cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase, and that especially in COS-7 cells, expression of 3b-EGFP was able to induce the increase of sub-G1 phase from 24 h after transfection, which was most obvious at 48 h. The apoptosis induction of 3b fusion protein in COS-7 cells was further confirmed by double cell labeling with 7-AAD and Annexin V, the function of 3b protein inducing cell G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis may provide a new insight for further study on the mechanism of SARS pathogenesis.
Figures
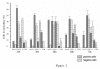
Similar articles
-
Over-expression of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3b protein induces both apoptosis and necrosis in Vero E6 cells.Virus Res. 2006 Dec;122(1-2):20-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2006.06.005. Epub 2006 Sep 11. Virus Res. 2006. PMID: 16965829 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolar localization of non-structural protein 3b, a protein specifically encoded by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.Virus Res. 2005 Dec;114(1-2):70-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2005.06.001. Epub 2005 Jul 25. Virus Res. 2005. PMID: 16046244 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial location of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3b protein.Mol Cells. 2006 Apr 30;21(2):186-91. Mol Cells. 2006. PMID: 16682811
-
SARS coronavirus 7a protein blocks cell cycle progression at G0/G1 phase via the cyclin D3/pRb pathway.Virology. 2006 Mar 1;346(1):74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.10.015. Epub 2005 Nov 21. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16303160 Free PMC article.
-
Unique SARS-CoV protein nsp1: bioinformatics, biochemistry and potential effects on virulence.Trends Microbiol. 2007 Feb;15(2):51-3. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2006.12.005. Epub 2007 Jan 4. Trends Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17207625 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enterovirus 71 mediates cell cycle arrest in S phase through non-structural protein 3D.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(3):425-36. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.980631. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25659038 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza A virus replication induces cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12832-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01216-10. Epub 2010 Sep 22. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20861262 Free PMC article.
-
Subacute thyroiditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection.Clin Case Rep. 2021 Nov 22;9(11):e05109. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.5109. eCollection 2021 Nov. Clin Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34849227 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitizing activity of a novel Benzoxazine through the promotion of apoptosis and inhibition of DNA repair.Invest New Drugs. 2014 Jun;32(3):424-35. doi: 10.1007/s10637-014-0079-4. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Invest New Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24627282
-
Coronavirus pathogenesis.Adv Virus Res. 2011;81:85-164. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385885-6.00009-2. Adv Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 22094080 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lang Z, Zhang L, Zhang S, Meng X, Li J, Song C, Sun L, Zhou Y. Pathological study on severe acute respiratory syndrome. Chin Med J (Engl) 2003;116:976–980. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

