Mammalian peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase mRNA expression can be modulated by the La autoantigen
- PMID: 16107699
- PMCID: PMC1190315
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.17.7505-7521.2005
Mammalian peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase mRNA expression can be modulated by the La autoantigen
Abstract
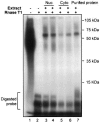
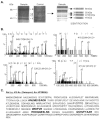
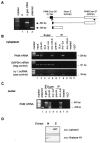
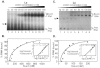
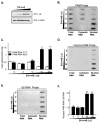
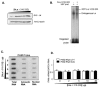
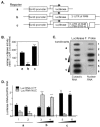
Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM; EC 1.14.17.3) catalyzes the COOH-terminal alpha-amidation of peptidylglycine substrates, yielding amidated products. We have previously reported a putative regulatory RNA binding protein (PAM mRNA-BP) that binds specifically to the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of PAM-mRNA. Here, the PAM mRNA-BP was isolated and revealed to be La protein using affinity purification onto a 3' UTR PAM RNA, followed by tandem mass spectrometry identification. We determined that the core binding sequence is approximately 15-nucleotides (nt) long and is located 471 nt downstream of the stop codon. Moreover, we identified the La autoantigen as a protein that specifically binds the 3' UTR of PAM mRNA in vivo and in vitro. Furthermore, La protein overexpression caused a nuclear retention of PAM mRNAs and resulted in the down-regulation of endogenous PAM activity. Most interestingly, the nuclear retention of PAM mRNA is lost upon expressing the La proteins that lack a conserved nuclear retention element, suggesting a direct association between PAM mRNA and La protein in vivo. Reporter assays using a chimeric mRNA that combined luciferase and the 3' UTR of PAM mRNA demonstrated a decrease of the reporter activity due to an increase in the nuclear localization of reporter mRNAs, while the deletion of the 15-nt La binding site led to their clear-cut cytoplasmic relocalization. The results suggest an important role for the La protein in the modulation of PAM expression, possibly by mechanisms that involve a nuclear retention and perhaps a processing of pre-PAM mRNA molecules.
Figures




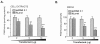

References
-
- Adilakshmi, T., and R. O. Laine. 2002. Ribosomal protein S25 mRNA partners with MTF-1 and La to provide a p53-mediated mechanism for survival or death. J. Biol. Chem. 277:4147-4151. - PubMed
-
- Alfano, C., D. Sanfelice, J. Babon, G. Kelly, A. Jacks, S. Curry, and M. R. Conte. 2004. Structural analysis of cooperative RNA binding by the La motif and central RRM domain of human La protein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11:323-329. - PubMed
-
- Ali, N., G. J. Pruijn, D. J. Kenan, J. D. Keene, and A. Siddiqui. 2000. Human La antigen is required for the hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. J. Biol. Chem. 275:27531-27540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
