Local translation of RhoA regulates growth cone collapse
- PMID: 16107849
- PMCID: PMC1317112
- DOI: 10.1038/nature03885
Local translation of RhoA regulates growth cone collapse
Abstract
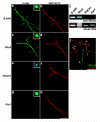
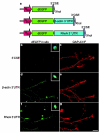
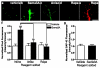
Neuronal development requires highly coordinated regulation of the cytoskeleton within the developing axon. This dynamic regulation manifests itself in axonal branching, turning and pathfinding, presynaptic differentiation, and growth cone collapse and extension. Semaphorin 3A (Sema3A), a secreted guidance cue that primarily functions to repel axons from inappropriate targets, induces cytoskeletal rearrangements that result in growth cone collapse. These effects require intra-axonal messenger RNA translation. Here we show that transcripts for RhoA, a small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) that regulates the actin cytoskeleton, are localized to developing axons and growth cones, and this localization is mediated by an axonal targeting element located in the RhoA 3' untranslated region (UTR). Sema3A induces intra-axonal translation of RhoA mRNA, and this local translation of RhoA is necessary and sufficient for Sema3A-mediated growth cone collapse. These studies indicate that local RhoA translation regulates the neuronal cytoskeleton and identify a new mechanism for the regulation of RhoA signalling.
Figures


References
-
- Gallo G, Letourneau PC. Regulation of growth cone actin filaments by guidance cues. Journal of Neurobiology. 2004;58:92–102. - PubMed
-
- Campbell DS, Holt CE. Chemotropic responses of retinal growth cones mediated by rapid local protein synthesis and degradation. Neuron. 2001;32:1013–26. - PubMed
-
- Luo Y, Raible D, Raper JA. Collapsin: a protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell. 1993;75:217–227. - PubMed
-
- Kolodkin AL, et al. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell. 1997;90:753–762. - PubMed
-
- He Z, Tessier-Lavigne M. Neuropilin is a receptor for the axonal chemorepellent Semaphorin III. Cell. 1997;90:739–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

