Animal virus replication and RNAi-mediated antiviral silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 16107851
- PMCID: PMC1388260
- DOI: 10.1038/nature03870
Animal virus replication and RNAi-mediated antiviral silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
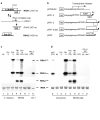
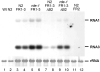
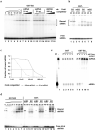
The worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a model system for studying many aspects of biology, including host responses to bacterial pathogens, but it is not known to support replication of any virus. Plants and insects encode multiple Dicer enzymes that recognize distinct precursors of small RNAs and may act cooperatively. However, it is not known whether the single Dicer of worms and mammals is able to initiate the small RNA-guided RNA interference (RNAi) antiviral immunity as occurs in plants and insects. Here we show complete replication of the Flock house virus (FHV) bipartite, plus-strand RNA genome in C. elegans. We show that FHV replication in C. elegans triggers potent antiviral silencing that requires RDE-1, an Argonaute protein essential for RNAi mediated by small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) but not by microRNAs. This immunity system is capable of rapid virus clearance in the absence of FHV B2 protein, which acts as a broad-spectrum RNAi inhibitor upstream of rde-1 by targeting the siRNA precursor. This work establishes a C. elegans model for genetic studies of animal virus-host interactions and indicates that mammals might use a siRNA pathway as an antiviral response.
Figures
References
-
- Mahajan-Miklos S, Tan MW, Rahme LG, Ausubel FM. Molecular mechanisms of bacterial virulence elucidated using a Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Caenorhabditis elegans pathogenesis model. Cell. 1999;96:47–56. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science. 1999;286:950–952. - PubMed
-
- Li HW, Li WX, Ding SW. Induction and suppression of RNA silencing by an animal virus. Science. 2002;296:1319–1321. - PubMed
-
- Fire A, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391:806–811. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

