Chemokine control of lymphocyte trafficking: a general overview
- PMID: 16108812
- PMCID: PMC1802414
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02183.x
Chemokine control of lymphocyte trafficking: a general overview
Abstract
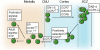
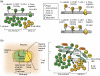
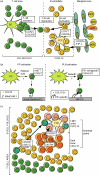
Chemokines are a large family of small, generally secreted polypeptides which guide lymphocyte movement throughout the body by controlling integrin avidity and inducing migration. Here, we look at recent, exciting findings on chemokine function throughout lymphocyte development and co-ordinated T and B cell migration during immune responses. Finally, we will review data on the regional control of immunity by tissue-specific chemokine receptors on effector/memory lymphocytes.
Figures
References
-
- Sprent J, Surh CD. T cell memory. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:551–79. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.100101.151926. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reif K, Cyster J. The CDM protein DOCK2 in lymphocyte migration. Trends Cell Biol. 2002;12:368–73. 10.1016/S0962-8924(02)02330-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cyster JG. Chemokines, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:127–59. - PubMed
-
- von Andrian UH, Mackay CR. T-cell function and migration. Two sides of the same coin. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1020–34. 10.1056/NEJM200010053431407. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cyster JG. Chemokines and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Science. 1999;286:2098–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

