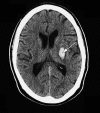
Should a patient with primary intracerebral haemorrhage receive antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy?
- PMID: 16110073
- PMCID: PMC1188113
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.331.7514.439
Should a patient with primary intracerebral haemorrhage receive antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy?
Figures
References
-
- Counsell C, Boonyakarnkul S, Dennis M, Sandercock P, Bamford J, Burn J, et al. Primary intracerebral haemorrhage in Oxford community stroke project 2. Prog Cerebrovasc Dis 1995;5: 26-34.
-
- Bailey RD, Hart RG, Benavante O, Pearce LA. Recurrent brain haemorrhage is more frequent than ischaemic stroke after intracranial haemorrhage. Neurology 2001;56: 773-7. - PubMed
-
- He J, Whelton PK, Vu B, Klag MJ. Aspirin and risk of haemorrhagic stroke; a meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. JAMA 1998;280: 1930-5. - PubMed
-
- Keir SL, Wardlaw JM, Sandercock PA, Chen Z. Antithrombotic therapy in patients with any form of intracranial haemorrhage: a systemic review of the available controlled studies. Cerebrovasc Dis 2002;14: 197-206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical