TWEAK induces liver progenitor cell proliferation
- PMID: 16110324
- PMCID: PMC1187931
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23486
TWEAK induces liver progenitor cell proliferation
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2005 Oct;115(10):2955. Baestcher, Manfred [corrected to Baetscher, Manfred]
Abstract
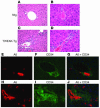
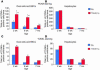
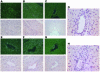
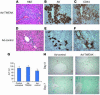
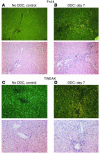
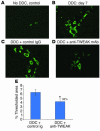
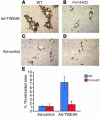
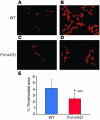
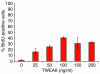
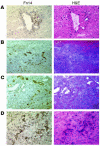
Progenitor ("oval") cell expansion accompanies many forms of liver injury, including alcohol toxicity and submassive parenchymal necrosis as well as experimental injury models featuring blocked hepatocyte replication. Oval cells can potentially become either hepatocytes or biliary epithelial cells and may be critical to liver regeneration, particularly when hepatocyte replication is impaired. The regulation of oval cell proliferation is incompletely understood. Herein we present evidence that a TNF family member called TWEAK (TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis) stimulates oval cell proliferation in mouse liver through its receptor Fn14. TWEAK has no effect on mature hepatocytes and thus appears to be selective for oval cells. Transgenic mice overexpressing TWEAK in hepatocytes exhibit periportal oval cell hyperplasia. A similar phenotype was obtained in adult wild-type mice, but not Fn14-null mice, by administering TWEAK-expressing adenovirus. Oval cell expansion induced by 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine (DDC) was significantly reduced in Fn14-null mice as well as in adult wild-type mice with a blocking anti-TWEAK mAb. Importantly, TWEAK stimulated the proliferation of an oval cell culture model. Finally, we show increased Fn14 expression in chronic hepatitis C and other human liver diseases relative to its expression in normal liver, which suggests a role for the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway in human liver injury. We conclude that TWEAK has a selective mitogenic effect for liver oval cells that distinguishes it from other previously described growth factors.
Figures

References
-
- Fausto N, Campbell JS. The role of hepatocytes and oval cells in liver regeneration and repopulation. Mech. Dev. 2003;120:117–130. - PubMed
-
- Tan J, et al. Immunohistochemical evidence for hepatic progenitor cells in liver diseases. Liver. 2002;22:365–373. - PubMed
-
- Libbrecht L, Roskams T. Hepatic progenitor cells in human liver diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002;13:389–396. - PubMed
-
- Roskams T. Progenitor cell involvement in cirrhotic human liver diseases: from controversy to consensus [review] J. Hepatol. 2003;39:431–434. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

