Calcium-dependent binding of calmodulin to neuronal gap junction proteins
- PMID: 16112650
- PMCID: PMC2222552
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.007
Calcium-dependent binding of calmodulin to neuronal gap junction proteins
Abstract
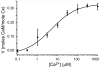
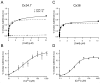
We examined the interactions of calmodulin with neuronal gap junction proteins connexin35 (Cx35) from perch, its mouse homologue Cx36, and the related perch Cx34.7 using surface plasmon resonance. Calmodulin bound to the C-terminal domains of all three connexins with rapid kinetics in a concentration- and Ca2+-dependent manner. Dissociation was also very rapid. K(d)'s for calmodulin binding at a high-affinity site ranged from 11 to 72 nM, and K(1/2)'s for Ca2+ were between 3 and 5 microM. No binding to the intracellular loops was observed. Binding competition experiments with synthetic peptides mapped the calmodulin binding site to a 10-30 amino acid segment at the beginning of the C-terminal domain of Cx36. The micromolar K(1/2)'s and rapid on and off rates suggest that this interaction may change dynamically in neurons, and may occur transiently when Ca2+ is elevated to a level that would occur in the near vicinity of an activated synapse.
Figures
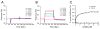
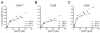

Similar articles
-
Calmodulin Binding to Connexin 35: Specializations to Function as an Electrical Synapse.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 1;21(17):6346. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176346. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32882943 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and expression of two related connexins from the perch retina define a distinct subgroup of the connexin family.J Neurosci. 1998 Oct 1;18(19):7625-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-19-07625.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9742134 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular interaction and functional regulation of connexin50 gap junctions by calmodulin.Biochem J. 2011 May 1;435(3):711-22. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101726. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21320072 Free PMC article.
-
Gap junction regulation by calmodulin.FEBS Lett. 2014 Apr 17;588(8):1430-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 16. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24440348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium Role in Gap Junction Channel Gating: Direct Electrostatic or Calmodulin-Mediated?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 10;25(18):9789. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189789. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calmodulin Binding to Connexin 35: Specializations to Function as an Electrical Synapse.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 1;21(17):6346. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176346. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32882943 Free PMC article.
-
Gap Junction Channel Regulation: A Tale of Two Gates-Voltage Sensitivity of the Chemical Gate and Chemical Sensitivity of the Fast Voltage Gate.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 12;25(2):982. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020982. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of intracellular calcium and pH in ischemic uncoupling of cardiac gap junction channels formed of connexins 43, 40, and 45: a critical function of C-terminal domain.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060506. Epub 2013 Mar 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23536911 Free PMC article.
-
A calcium-dependent pathway underlies activity-dependent plasticity of electrical synapses in the thalamic reticular nucleus.J Physiol. 2017 Jul 1;595(13):4417-4430. doi: 10.1113/JP274049. Epub 2017 May 26. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28369952 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin 35/36 is phosphorylated at regulatory sites in the retina.Vis Neurosci. 2007 May-Jun;24(3):363-75. doi: 10.1017/S095252380707037X. Epub 2007 Jul 20. Vis Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17640446 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

