Isolation and partial purification of macrophage- and dendritic cell-activating components from Mycoplasma arthritidis: association with organism virulence and involvement with Toll-like receptor 2
- PMID: 16113324
- PMCID: PMC1231055
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.6039-6047.2005
Isolation and partial purification of macrophage- and dendritic cell-activating components from Mycoplasma arthritidis: association with organism virulence and involvement with Toll-like receptor 2
Abstract
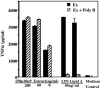
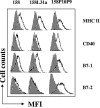
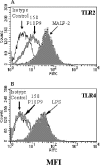
Mycoplasma arthritidis induces toxicity, arthritis, and dermal necrosis in mice. Virulence factors include a superantigen and membrane adhesins and possibly also a bacteriophage component. Here we compare the biological properties of Triton X-114 extracts derived from avirulent and virulent M. arthritidis strains. Macrophage cell lines and resident peritoneal macrophages were used to assess inflammatory potential as indicated by production of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, and/or nitric oxide. The activity resided exclusively within the hydrophobic detergent phase, was unaffected by heat treatment at 100 degrees C for 30 min, and was resistant to proteinase K digestion, suggesting involvement of a lipopeptide. Contamination of extracts with endotoxin or superantigen was excluded. Extracts of the more virulent strain had higher activity than did those of the avirulent strain. Using CHO cells expressing Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) or TLR4, both with transfected CD14, we showed that extracts activated these cells via TLR2 but not by TLR4. Also, macrophages from C57BL/6 TLR2(-/-) mice failed to respond to the extracts, whereas those from TLR2(+/+) cells did respond. The preparations from the virulent strain of M. arthritidis were also more potent in activating dendritic cells, as evidenced by up-regulation of major histocompatibility complex class II, CD40, B7-1, and B7-2. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and subsequent elution of gel slices revealed the presence of three active moieties which corresponded to molecular masses of approximately 24, 28, and 40 kDa. Three active components were also found by reverse-phase chromatography. We suggest that macrophage activation by M. arthritidis could play a significant role in the inflammatory response induced in the host by this organism.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Inflammatory lipoproteins purified from a toxigenic and arthritogenic strain of Mycoplasma arthritidis are dependent on Toll-like receptor 2 and CD14.Infect Immun. 2007 Apr;75(4):1820-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00516-06. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17283106 Free PMC article.
-
TLR2 and TLR4 differentially regulate B7-1 resulting in distinct cytokine responses to the mycoplasma superantigen MAM as well as to disease induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis.Cell Microbiol. 2006 Mar;8(3):414-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00630.x. Cell Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16469054
-
Novel interactions of a microbial superantigen with TLR2 and TLR4 differentially regulate IL-17 and Th17-associated cytokines.Cell Microbiol. 2011 Mar;13(3):374-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01540.x. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Cell Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 20946245
-
The immunobiology of Mycoplasma arthritidis and its superantigen MAM.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;174:107-19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50998-8_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991. PMID: 1802617 Review. No abstract available.
-
The Mycoplasma arthritidis T-cell mitogen, MAM: a model superantigen.Immunol Today. 1991 Aug;12(8):271-6. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90125-D. Immunol Today. 1991. PMID: 1910449 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory lipoproteins purified from a toxigenic and arthritogenic strain of Mycoplasma arthritidis are dependent on Toll-like receptor 2 and CD14.Infect Immun. 2007 Apr;75(4):1820-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00516-06. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17283106 Free PMC article.
-
Murine toll-like receptor 2 activation induces type I interferon responses from endolysosomal compartments.PLoS One. 2010 Apr 20;5(4):e10250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010250. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20422028 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying genome-wide immune gene variation underlying infectious disease in wildlife populations - a next generation sequencing approach in the gopher tortoise.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jan 19;19(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4452-0. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29351737 Free PMC article.
-
Design of PCR-based method for detection of a gene-encoding Mycoplasma arthritidis mitogen superantigen in synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients.Iran J Microbiol. 2014 Dec;6(6):415-20. Iran J Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25926960 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Mycoplasma hominis PG21 with Human Dendritic Cells: Interleukin-23-Inducing Mycoplasmal Lipoproteins and Inflammasome Activation of the Cell.J Bacteriol. 2017 Jul 11;199(15):e00213-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00213-17. Print 2017 Aug 1. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28559291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira, S., and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:499-511. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, K. V., G. Jurgens, and C. Nusslein-Volhard. 1985. Establishment of dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo: genetic studies on the role of the Toll gene product. Cell 42:779-789. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, B. 2004. Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature 430:257-263. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, B. 2000. Tlr4: central component of the sole mammalian LPS sensor. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 12:20-26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

