Horizontally acquired genes for purine salvage in Borrelia spp. causing relapsing fever
- PMID: 16113341
- PMCID: PMC1231056
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.6165-6168.2005
Horizontally acquired genes for purine salvage in Borrelia spp. causing relapsing fever
Abstract
Unlike Borrelia burgdorferi, the relapsing fever agent Borrelia hermsii and the related Borrelia miyamotoi had purA and purB genes of the purine salvage pathway. These were located among the rRNA genes. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that these genes had a different evolutionary history than those of orthologs in other spirochetes.
Figures
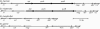

References
-
- Barbour, A. G. 2001. Borrelia: a diverse and ubiquitous genus of tick-borne pathogens, p. 153-174. In W. M. Scheld, W. A. Craig, and J. M. Hughes (ed.), Emerging infections 5. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
-
- Casjens, S., N. Palmer, R. van Vugt, W. M. Huang, B. Stevenson, P. Rosa, R. Lathigra, G. Sutton, J. Peterson, R. J. Dodson, D. Haft, E. Hickey, M. Gwinn, O. White, and C. M. Fraser. 2000. A bacterial genome in flux: the twelve linear and nine circular extrachromosomal DNAs in an infectious isolate of the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol. Microbiol. 35:490-516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

