Comparison of different techniques for purification of triamcinolone acetonide suspension for intravitreal use
- PMID: 16113361
- PMCID: PMC1772839
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2005.067744
Comparison of different techniques for purification of triamcinolone acetonide suspension for intravitreal use
Abstract
Background: Intravitreal triamcinolone has increasingly been used for the treatment of oedematous and neovascular diseases and purification of triamcinolone suspension may be important in order to avoid the potential toxic effects of the vehicle. The aim was to evaluate different techniques used to reduce the solvent agent benzyl alcohol (9.9 mg/ml) from a commercially prepared triamcinolone acetonide suspension.
Methods: Different techniques were used to reduce the solvent agent benzyl alcohol: filter techniques using 0.22 mum or 5 mum pore size, and non-filter techniques using sedimentation or centrifugation. Quantification of triamcinolone acetonide and benzyl alcohol was performed by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC).
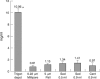
Results: Benzyl alcohol concentration was decreased significantly in all the techniques used compared with the original commercial suspension (p<0.05), with no significant differences among them. The reduction was approximately one tenth of its original concentration. However, triamcinolone acetonide concentration differed significantly depending on the method used. Centrifugation method showed no differences versus the original commercial solution; sedimentation technique reduced the expected dose only 25%; the filter technique using a 5 mum pore size membrane reduced the expected dose to one fourth, while the filter technique using a 0.22 mum pore size membrane reduced the expected dose to 45%.
Conclusions: All the different techniques employed effectively reduced the concentration of benzyl alcohol. However, the final concentration of triamcinolone was much lower than expected using the filter techniques. The pore size membrane inversely influenced the final concentration, with part of the triamcinolone crystals probably being entrapped in the filter. Centrifugation is recommended as the best way of administering the drug.
Figures

Comment in
-
Purification of triamcinolone acetonide suspension for intravitreal injection.Br J Ophthalmol. 2006 Jan;90(1):123-4. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2005.083501. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006. PMID: 16361689 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Influence of different purification techniques on triamcinolone yield and particle size spectrum.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007 May;245(5):689-96. doi: 10.1007/s00417-006-0436-x. Epub 2006 Sep 28. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 17006679
-
Removal of benzyl alcohol from a commercially available triamcinolone acetonide suspension for intravitreal use.Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2006 Mar-Apr;37(2):162-4. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging. 2006. PMID: 16583642
-
[Triamcinolone acetonide without solvents].Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2012 Oct;87(10):320-3. doi: 10.1016/j.oftal.2012.04.005. Epub 2012 May 30. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2012. PMID: 23021229 Spanish.
-
Intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide for treatment of intraocular oedematous and neovascular diseases.Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005 Dec;83(6):645-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0420.2005.00592.x. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2005. PMID: 16396641 Review.
-
[Treatment of oedematous, proliferative and neovascular diseases by intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2003 Jun;220(6):384-90. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-40272. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2003. PMID: 12830391 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Influence of different purification techniques on triamcinolone yield and particle size spectrum.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007 May;245(5):689-96. doi: 10.1007/s00417-006-0436-x. Epub 2006 Sep 28. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 17006679
-
Triamcinolone crystal size.Ophthalmology. 2010 Aug;117(8):1654, 1654.e1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.01.052. Ophthalmology. 2010. PMID: 20682380 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comparison of 4 mg versus 20 mg intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injections.Br J Ophthalmol. 2008 Jun;92(6):810-3. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2007.126227. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 18420748 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Intravitreal Injection of Filtered Modified Low-Dose Triamcinolone Acetonide and Ranibizumab on Pseudophakic Cystoid Macular Edema.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 16;9:777549. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.777549. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35252233 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetic behavior of intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide prepared by a hospital pharmacy.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2008 Nov-Dec;52(6):489-492. doi: 10.1007/s10384-008-0584-0. Epub 2008 Dec 17. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 19089571
References
-
- Jonas JB, Hayler JK, Söfker A, et al. Regression of neovascular iris vessels by intravitreal injection of crystalline cortisone. J Glaucoma 2001;10:284–7. - PubMed
-
- Martidis A , Duker JS, Greenberg PB, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone for refractory diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 2002;109:920–7. - PubMed
-
- Jonas JB, Kreissig I, Söfker A, et al. Intravitreal injection of intravitreal triamcinolone for diffuse diabetic macular edema. Arch Ophthalmol 2003;121:57–61. - PubMed
-
- Antcliff RJ, Spalton DJ, Stanford MR, et al. Intravitreal triamcinolone for uveitic cystoid macular edema: an optical coherence tomography study. Ophthalmology 2001;108:765–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
