Glucose transporter 1 expression identifies a population of cycling CD4+ CD8+ human thymocytes with high CXCR4-induced chemotaxis
- PMID: 16126902
- PMCID: PMC1200272
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0503603102
Glucose transporter 1 expression identifies a population of cycling CD4+ CD8+ human thymocytes with high CXCR4-induced chemotaxis
Abstract
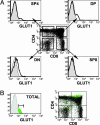
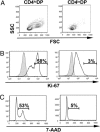
GLUT1, the major glucose transporter in peripheral T lymphocytes, is induced upon T cell receptor activation. However, the role of GLUT1 during human thymocyte differentiation remains to be evaluated. Our identification of GLUT1 as the human T lymphotrophic virus (HTLV) receptor has enabled us to use tagged HTLV-receptor-binding domain fusion proteins to specifically monitor surface GLUT1 expression. Here, we identify a unique subset of CD4+ CD8+ double-positive (DP) thymocytes, based on their GLUT1 surface expression. Whereas these cells express variable levels of CD8, they express uniformly high levels of CD4. Glucose uptake was 7-fold higher in CD4(hi) DP thymocytes than in CD4(lo) DP thymocytes (P = 0.0002). Further analyses indicated that these GLUT1+ thymocytes are early post-beta-selection, as demonstrated by low levels of T cell receptor (TCR)alphabeta and CD3. This population of immature GLUT1+ DP cells is rapidly cycling and can be further distinguished by specific expression of the transferrin receptor. Importantly, the CXCR4 chemokine receptor is expressed at 15-fold higher levels on GLUT1+ DP thymocytes, as compared with the DP GLUT1- subset, and the former cells show enhanced chemotaxis to the CXCR4 ligand CXCL12. Thus, during human thymopoiesis, GLUT1 is up-regulated after beta-selection, and these immature DP cells constitute a population with distinct metabolic and chemotactic properties.
Figures




References
-
- Mueckler, M., Caruso, C., Baldwin, S. A., Panico, M., Blench, I., Morris, H. R., Allard, W. J., Lienhard, G. E. & Lodish, H. F. (1985) Science 229, 941-945. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti, R., Jung, C. Y., Lee, T. P., Liu, H. & Mookerjee, B. K. (1994) J. Immunol. 152, 2660-2668. - PubMed
-
- Rathmell, J. C., Elstrom, R. L., Cinalli, R. M. & Thompson, C. B. (2003) Eur. J. Immunol. 33, 2223-2232. - PubMed
-
- Frauwirth, K. A., Riley, J. L., Harris, M. H., Parry, R. V., Rathmell, J. C., Plas, D. R., Elstrom, R. L., June, C. H. & Thompson, C. B. (2002) Immunity 16, 769-777. - PubMed
-
- Cooper, E. H., Barkhan, P. & Hale, A. J. (1963) Br. J. Haematol. 9, 101-111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

