A SUMOylation-dependent pathway mediates transrepression of inflammatory response genes by PPAR-gamma
- PMID: 16127449
- PMCID: PMC1464798
- DOI: 10.1038/nature03988
A SUMOylation-dependent pathway mediates transrepression of inflammatory response genes by PPAR-gamma
Abstract
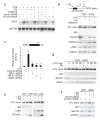
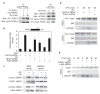
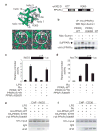
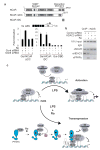
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-gamma) has essential roles in adipogenesis and glucose homeostasis, and is a molecular target of insulin-sensitizing drugs. Although the ability of PPAR-gamma agonists to antagonize inflammatory responses by transrepression of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) target genes is linked to antidiabetic and antiatherogenic actions, the mechanisms remain poorly understood. Here we report the identification of a molecular pathway by which PPAR-gamma represses the transcriptional activation of inflammatory response genes in mouse macrophages. The initial step of this pathway involves ligand-dependent SUMOylation of the PPAR-gamma ligand-binding domain, which targets PPAR-gamma to nuclear receptor corepressor (NCoR)-histone deacetylase-3 (HDAC3) complexes on inflammatory gene promoters. This in turn prevents recruitment of the ubiquitylation/19S proteosome machinery that normally mediates the signal-dependent removal of corepressor complexes required for gene activation. As a result, NCoR complexes are not cleared from the promoter and target genes are maintained in a repressed state. This mechanism provides an explanation for how an agonist-bound nuclear receptor can be converted from an activator of transcription to a promoter-specific repressor of NF-kappaB target genes that regulate immunity and homeostasis.
Figures
References
-
- Lehmann JM, et al. An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) J Biol Chem. 1995;270:12953–12956. - PubMed
-
- Spiegelman BM. PPARγ: adipogenic regulator and thiazolidinedione receptor. Diabetes. 1998;47:507–514. - PubMed
-
- Willson TM, Lambert MH, Kliewer SA. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and metabolic disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:341–67. - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM, et al. Effect of rosiglitazone treatment on nontraditional markers of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2002;106:679–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

