Intradiscal pressure measurements in normal discs, compressed discs and compressed discs treated with axial posterior disc distraction: an experimental study on the rabbit lumbar spine model
- PMID: 16133080
- PMCID: PMC3489348
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-005-0953-z
Intradiscal pressure measurements in normal discs, compressed discs and compressed discs treated with axial posterior disc distraction: an experimental study on the rabbit lumbar spine model
Abstract
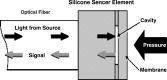
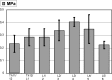
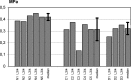
Intervertebral disc (IVD) pressure measurement is an appropriate method for characterizing spinal loading conditions. However, there is no human or animal model that provides sufficient IVD pressure data. The aim of our study was to establish physiological pressure values in the rabbit lumbar spine and to determine whether temporary external disc compression and distraction were associated with pressure changes. Measurements were done using a microstructure-based fibreoptic sensor. Data were collected in five control rabbits (N, measurement lying prone at segment L3/4 at day 28), five rabbits with 28 days of axial compression (C, measurement at day 28) and three rabbits with 28 days of axial compression and following 28 days of axial distraction (D, measurement at day 56). Disc compression and distraction was verified by disc height in lateral radiographs. The controls (N) showed a level-related range between 0.25 MPa-0.45 MPa. The IVD pressure was highest at level L3/4 (0.42 MPa; range 0.38-0.45) with a decrease in both cranial and caudal adjacent segments. The result for C was a significant decrease in IVD pressure (0.31 MPa) when compared with controls (P=0.009). D showed slightly higher median IVD pressure (0.32 MPa) compared to C, but significantly lower levels when compared with N (P=0.037). Our results indicate a high range of physiological IVD pressure at different levels of the lumbar rabbit spine. Temporary disc compression reduces pressure when compared with controls. These data support the hypothesis that temporary external compression leads to moderate disc degeneration as a result of degradation of water-binding disc matrix or affected active pumping mechanisms of nutrients into the disc. A stabilization of IVD pressure in discs treated with temporary distraction was observed.
Figures
References
-
- Castagnera L, Grenier N, Lavignolle B, Greselle JF, Senegas J, Caille JM. Study of correlation between intradiscal pressure and magnetic resonance imaging data in evaluation of disc degeneration. Therapeutic issue with percutaneus nucleotomy. Spine. 1991;16(3):348–352. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Baer AE, Paik PY, Yan W, Setton LA (2002) Matrix protein gene expression in intervertebral disc cells subjected to altered osmolarity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 10;293(3):932–938 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

