The adjuvant activity of CpG DNA requires T-bet expression in dendritic cells
- PMID: 16135562
- PMCID: PMC1201626
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506638102
The adjuvant activity of CpG DNA requires T-bet expression in dendritic cells
Abstract
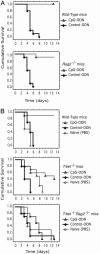
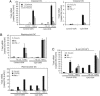
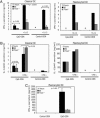
Treatment with synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides containing CpG motifs (CpG ODNs) is remarkably protective against otherwise lethal infection. Here, we describe an essential role for the transcription factor T-bet in mediating the protective function of CpG ODNs. Loss of T-bet in conventional CD11c(hi) dendritic cells (DCs) and in plasmacytoid DCs impaired production of IFNs. Strikingly, in contrast to Rag2-/- mice, Rag2-/- mice that also lacked T-bet (DKO) could not be rescued from lethal Listeria monocytogenes infection by prior treatment with CpG ODN. Rescue was achieved by adoptive transfer of CD11c(hi) DCs from WT, but not T-bet-/-, CpG ODN-treated donor mice. We conclude that T-bet in DCs is required for the adjuvant activity of CpG ODN in infection, revealing its vital role in innate immunity.
Figures

References
-
- Krieg, A. M. (2002) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 709-760. - PubMed
-
- Krieg, A. M. (2001) Trends Microbiol. 9, 249-252. - PubMed
-
- Ishii, K. J., Gursel, I., Gursel, M. & Klinman, D. M. (2004) Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 6, 166-174. - PubMed
-
- Edelson, B. T. & Unanue, E. R. (2000) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 12, 425-431. - PubMed
-
- Pamer, E. G. (2004) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 812-823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

