Structural basis for the interaction of Bordetella pertussis adenylyl cyclase toxin with calmodulin
- PMID: 16138079
- PMCID: PMC1224690
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600800
Structural basis for the interaction of Bordetella pertussis adenylyl cyclase toxin with calmodulin
Abstract
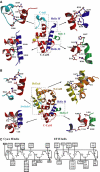
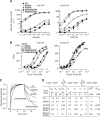
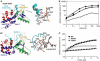
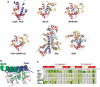
CyaA is crucial for colonization by Bordetella pertussis, the etiologic agent of whooping cough. Here we report crystal structures of the adenylyl cyclase domain (ACD) of CyaA with the C-terminal domain of calmodulin. Four discrete regions of CyaA bind calcium-loaded calmodulin with a large buried contact surface. Of those, a tryptophan residue (W242) at an alpha-helix of CyaA makes extensive contacts with the calcium-induced, hydrophobic pocket of calmodulin. Mutagenic analyses show that all four regions of CyaA contribute to calmodulin binding and the calmodulin-induced conformational change of CyaA is crucial for catalytic activation. A crystal structure of CyaA-calmodulin with adefovir diphosphate, the metabolite of an approved antiviral drug, reveals the location of catalytic site of CyaA and how adefovir diphosphate tightly binds CyaA. The ACD of CyaA shares a similar structure and mechanism of activation with anthrax edema factor (EF). However, the interactions of CyaA with calmodulin completely diverge from those of EF. This provides molecular details of how two structurally homologous bacterial toxins evolved divergently to bind calmodulin, an evolutionarily conserved calcium sensor.
Figures



References
-
- Abrami L, Reig N, van der Goot FG (2005) Anthrax toxin: the long and winding road that leads to the kill. Trends Microbiol 13: 72–78 - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL (2003) Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 517–529 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya S, Bunick CG, Chazin WJ (2004) Target selectivity in EF-hand calcium binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1742: 69–79 - PubMed
-
- Bouhss A, Krin E, Munier H, Gilles AM, Danchin A, Glaser P, Barzu O (1993) Cooperative phenomena in binding and activation of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase by calmodulin. J Biol Chem 268: 1690–1694 - PubMed
-
- Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL (1998) Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 54: 905–921 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

