Mechanism of Lys48-linked polyubiquitin chain recognition by the Mud1 UBA domain
- PMID: 16138082
- PMCID: PMC1224687
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600797
Mechanism of Lys48-linked polyubiquitin chain recognition by the Mud1 UBA domain
Abstract
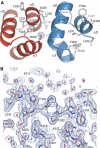
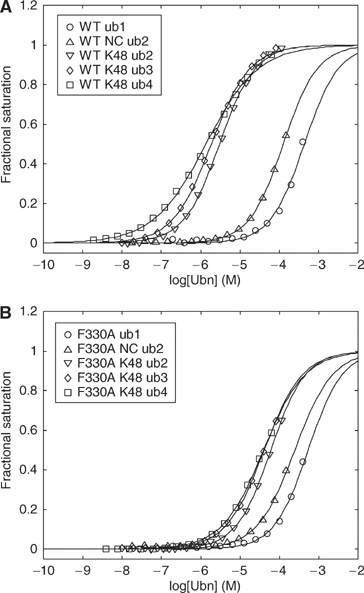
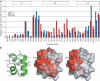
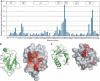
The ubiquitin-pathway associated (UBA) domain is a 40-residue polyubiquitin-binding motif. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe protein Mud1 is an ortholog of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA-damage response protein Ddi1 and binds to K48-linked polyubiquitin through its UBA domain. We have solved the crystal structure of Mud1 UBA at 1.8 angstroms resolution, revealing a canonical three-helical UBA fold. We have probed the interactions of this domain using mutagenesis, surface plasmon resonance, NMR and analytical ultracentrifugation. We show that the ubiquitin-binding surface of Mud1 UBA extends beyond previously recognized motifs and can be functionally dissected into primary and secondary ubiquitin-binding sites. Mutation of Phe330 to alanine, a residue exposed between helices 2 and 3, significantly reduces the affinity of the Mud1 UBA domain for K48-linked polyubiquitin, despite leaving the primary binding surface functionally intact. Moreover, K48-linked diubiquitin binds a single Mud1 UBA domain even in the presence of excess UBA. We therefore propose a mechanism for the recognition of K48-linked polyubiquitin chains by Mud1 in which diubiquitin units are specifically recognized by a single UBA domain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural determinants for selective recognition of a Lys48-linked polyubiquitin chain by a UBA domain.Mol Cell. 2005 Jun 10;18(6):687-98. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.05.013. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15949443
-
Click synthesis of ubiquitin dimer analogs to interrogate linkage-specific UBA domain binding.Chem Commun (Camb). 2012 Jan 7;48(2):296-8. doi: 10.1039/c1cc15834a. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Chem Commun (Camb). 2012. PMID: 22095407
-
Affinity makes the difference: nonselective interaction of the UBA domain of Ubiquilin-1 with monomeric ubiquitin and polyubiquitin chains.J Mol Biol. 2008 Mar 14;377(1):162-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.12.029. Epub 2007 Dec 23. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18241885 Free PMC article.
-
UBA domain containing proteins in fission yeast.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003 May;35(5):629-36. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00393-x. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12672455 Review.
-
Structural and functional studies of mutations affecting the UBA domain of SQSTM1 (p62) which cause Paget's disease of bone.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Nov;32(Pt 5):728-30. doi: 10.1042/BST0320728. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15493999 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel TDP2-ubiquitin interactions and their importance for the repair of topoisomerase II-mediated DNA damage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Dec 1;44(21):10201-10215. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw719. Epub 2016 Aug 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27543075 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-damage-inducible 1 protein (Ddi1) contains an uncharacteristic ubiquitin-like domain that binds ubiquitin.Structure. 2015 Mar 3;23(3):542-557. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2015.01.010. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Structure. 2015. PMID: 25703377 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial transcription factor TFAM coordinates the assembly of multiple DNA molecules into nucleoid-like structures.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Sep;18(9):3225-36. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0404. Epub 2007 Jun 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17581862 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domain of p62 and its interaction with ubiquitin.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 9;286(36):31864-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.259630. Epub 2011 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21715324 Free PMC article.
-
Specific recognition of linear ubiquitin chains by the Npl4 zinc finger (NZF) domain of the HOIL-1L subunit of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Dec 20;108(51):20520-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109088108. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 22139374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertolaet BL, Clarke DJ, Wolff M, Watson MH, Henze M, Divita G, Reed SI (2001a) UBA domains mediate protein–protein interactions between two DNA damage-inducible proteins. J Mol Biol 313: 955–963 - PubMed
-
- Bertolaet BL, Clarke DJ, Wolff M, Watson MH, Henze M, Divita G, Reed SI (2001b) UBA domains of DNA damage-inducible proteins interact with ubiquitin. Nat Struct Biol 8: 417–422 - PubMed
-
- Bochtler M, Ditzel L, Groll M, Hartmann C, Huber R (1999) The proteasome. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 28: 295–317 - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Pickart CM (1990) A 25-kilodalton ubiquitin carrier protein (E2) catalyzes multi-ubiquitin chain synthesis via lysine 48 of ubiquitin. J Biol Chem 265: 21835–21842 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

