Mechanisms of sudden cardiac death
- PMID: 16138184
- PMCID: PMC1193893
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI26381
Mechanisms of sudden cardiac death
Abstract
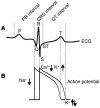
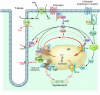
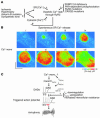
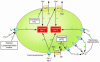
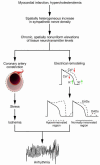
Despite recent advances in preventing sudden cardiac death (SCD) due to cardiac arrhythmia, its incidence in the population at large has remained unacceptably high. Better understanding of the interaction among various functional, structural, and genetic factors underlying the susceptibility to, and initiation of, fatal arrhythmias is a major goal and will provide new tools for the prediction, prevention, and therapy of SCD. Here, we review the role of aberrant intracellular Ca handling, ionic imbalances associated with acute myocardial ischemia, neurohumoral changes, and genetic predisposition in the pathogenesis of SCD due to cardiac arrhythmia. Therapeutic measures to prevent SCD are also discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Huikuri HV, Castellanos A, Myerburg RJ. Sudden death due to cardiac arrhythmias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;345:1473–1482. - PubMed
-
- Yadav AV, Das M, Zipes DP. Selection of patients for ICDs: ‘where are we in 2005?’. ACC Curr. J. Review. 2005;14:33–37.
-
- Echt DS, et al. Mortality and morbidity in patients receiving encainide, flecainide, or placebo: the Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991;324:781–788. - PubMed
-
- Gottlieb SS, McCarter RJ, Vogel RA. Effect of beta-blockade on mortality among high-risk and low-risk patients after myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998;339:489–497. - PubMed
-
- Alberte C, Zipes DP. Use of nonantiarrhythmic drugs for prevention of sudden cardiac death. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2003;14:S87–S95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

