The let-7 MicroRNA family members mir-48, mir-84, and mir-241 function together to regulate developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 16139228
- PMCID: PMC3969732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.07.009
The let-7 MicroRNA family members mir-48, mir-84, and mir-241 function together to regulate developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
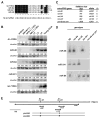
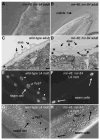
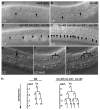
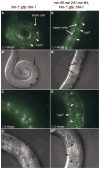
The microRNA let-7 is a critical regulator of developmental timing events at the larval-to-adult transition in C. elegans. Recently, microRNAs with sequence similarity to let-7 have been identified. We find that doubly mutant animals lacking the let-7 family microRNA genes mir-48 and mir-84 exhibit retarded molting behavior and retarded adult gene expression in the hypodermis. Triply mutant animals lacking mir-48, mir-84, and mir-241 exhibit repetition of L2-stage events in addition to retarded adult-stage events. mir-48, mir-84, and mir-241 function together to control the L2-to-L3 transition, likely by base pairing to complementary sites in the hbl-1 3' UTR and downregulating hbl-1 activity. Genetic analysis indicates that mir-48, mir-84, and mir-241 specify the timing of the L2-to-L3 transition in parallel to the heterochronic genes lin-28 and lin-46. These results indicate that let-7 family microRNAs function in combination to affect both early and late developmental timing decisions.
Figures
References
-
- Abrahante JE, Daul AL, Li M, Volk ML, Tennessen JM, Miller EA, Rougvie AE. The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev. Cell. 2003;4:625–637. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. A hierarchy of regulatory genes controls a larva-to-adult developmental switch in C. elegans. Cell. 1989;57:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V, Horvitz HR. Heterochronic mutants of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1984;226:409–416. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V, Lee RC, Lavanway A, Williams PT, Jewell D. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr Biol. 2003;13:807–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

