Attenuation of methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice by systemic administration of naltrexone
- PMID: 16140168
- PMCID: PMC3138078
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2005.05.028
Attenuation of methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice by systemic administration of naltrexone
Abstract
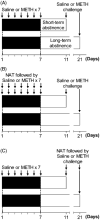
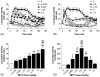
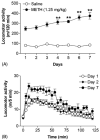
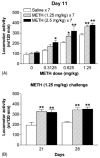
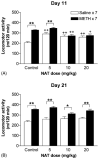
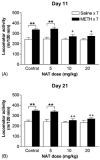
Repeated intermittent exposure to psychostimulants was found to produce behavioral sensitization. The present study was designed to establish a mouse model and by which to investigate whether opioidergic system plays a role in methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization. Mice injected with 2.5 mg/kg of methamphetamine once a day for 7 consecutive days showed behavioral sensitization after challenge with 0.3125 mg/kg of the drug on day 11, whereas mice injected with a lower daily dose (1.25 mg/kg) did not. Mice received daily injections with either 1.25 or 2.5 mg/kg of methamphetamine showed behavioral sensitization after challenge with 1.25 mg/kg of the drug on days 11, 21, and 28. To investigate the role of opioidergic system in the induction and expression of behavioral sensitization, long-acting but non-selective opioid antagonist naltrexone was administrated prior to the daily injections of and challenge with methamphetamine, respectively. Our results show that the expressions of behavioral sensitization were attenuated by pretreatment with 10 or 20 mg/kg of naltrexone either during the induction period or before methamphetamine challenge when they were tested on days 11 and 21. These results indicate that repeated injection with methamphetamine dose-dependently induced behavioral sensitization in mice, and suggest the involvement of opioid receptors in the induction and expression of methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization.
Figures
References
-
- Adams DH, Hanson GR, Keefe KA. Cocaine and metham-phetamine differentially affect opioid peptide mRNA expression in the striatum. J Neurochem. 2000;75:2061–2070. - PubMed
-
- Adams DH, Hanson GR, Keefe KA. Distinct effects of metham-phetamine and cocaine on preprodynorphin messenger RNA in rat striatal patch and matrix. J Neurochem. 2003;84:87–93. - PubMed
-
- Anggadiredja K, Sakimura K, Hiranita T, Yamamoto T. Naltrexone attenuates cue- but not drug-induced methamphetamine seeking: a possible mechanism for the dissociation of primary and secondary reward. Brain Res. 2004;1021:272–276. - PubMed
-
- Badiani A, Anagnostaras SG, Robinson TE. The development of sensitization to the psychomotor stimulant effects of amphetamine is enhanced in a novel environment. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 1995;117:443–452. - PubMed
-
- Badiani A, Oates MM, Fraioli S, Browman KE, Ostrander MM, Xue CJ, Wolf ME, Robinson TE. Environmental modulation of the response to amphetamine: dissociation between changes in behavior and changes in dopamine and glutamate overflow in the rat striatal complex. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 2000;151:166–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

