Antimicrobial peptides from amphibian skin potently inhibit human immunodeficiency virus infection and transfer of virus from dendritic cells to T cells
- PMID: 16140737
- PMCID: PMC1212620
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.18.11598-11606.2005
Antimicrobial peptides from amphibian skin potently inhibit human immunodeficiency virus infection and transfer of virus from dendritic cells to T cells
Abstract
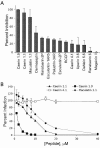
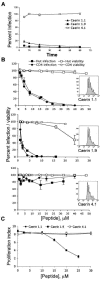
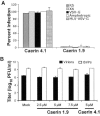
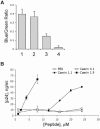
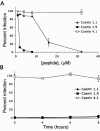
Topical antimicrobicides hold great promise in reducing human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transmission. Amphibian skin provides a rich source of broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptides including some that have antiviral activity. We tested 14 peptides derived from diverse amphibian species for the capacity to inhibit HIV infection. Three peptides (caerin 1.1, caerin 1.9, and maculatin 1.1) completely inhibited HIV infection of T cells within minutes of exposure to virus at concentrations that were not toxic to target cells. These peptides also suppressed infection by murine leukemia virus but not by reovirus, a structurally unrelated nonenveloped virus. Preincubation with peptides prevented viral fusion to target cells and disrupted the HIV envelope. Remarkably, these amphibian peptides also were highly effective in inhibiting the transfer of HIV by dendritic cells (DCs) to T cells, even when DCs were transiently exposed to peptides 8 h after virus capture. These data suggest that amphibian-derived peptides can access DC-sequestered HIV and destroy the virus before it can be transferred to T cells. Thus, amphibian-derived antimicrobial peptides show promise as topical inhibitors of mucosal HIV transmission and provide novel tools to understand the complex biology of HIV capture by DCs.
Figures
References
-
- Ali, M. F., K. R. Lips, F. C. Knoop, B. Fritzsch, C. Miller, and J. M. Conlon. 2002. Antimicrobial peptides and protease inhibitors in the skin secretions of the crawfish frog, Rana areolata. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1601:55-63. - PubMed
-
- Balla, M. S., J. H. Bowie, and F. Separovic. 2004. Solid-state NMR study of antimicrobial peptides from Australian frogs in phospholipid membranes. Eur. Biophys. J. 33:109-116. - PubMed
-
- Barton, E. S., J. C. Forrest, J. L. Connolly, J. D. Chappell, Y. Liu, F. Schnell, A. Nusrat, C. A. Parkos, and T. S. Dermody. 2001. Junction adhesion molecule is a receptor for reovirus. Cell 104:441-451. - PubMed
-
- Belaid, A., M. Aouni, R. Khelifa, A. Trabelsi, M. Jemmali, and K. Hani. 2002. In vitro antiviral activity of dermaseptins against herpes simplex virus type 1. J. Med. Virol. 66:229-234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

