The UNC-73/Trio RhoGEF-2 domain is required in separate isoforms for the regulation of pharynx pumping and normal neurotransmission in C. elegans
- PMID: 16140983
- PMCID: PMC1199572
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1319905
The UNC-73/Trio RhoGEF-2 domain is required in separate isoforms for the regulation of pharynx pumping and normal neurotransmission in C. elegans
Abstract
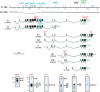
In both Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila, UNC-73/Trio functions in axon guidance by signaling through the Rac GTPase to regulate cytoskeletal rearrangements necessary for growth cone migrations. Here, we show that the complex C. elegans unc-73 gene encodes at least eight differentially expressed UNC-73 intracellular protein isoforms. Previously reported mutations affecting UNC-73 isoforms encoding the Rac-specific RhoGEF-1 domain cause uncoordinated movement, correlating with defects in axon guidance. Mutations in isoforms encoding the Rho-specific RhoGEF-2 domain, which we describe here, result in L1 stage larval lethality with no associated axon guidance defects. Isoform-specific rescue experiments reveal separate functions for the various RhoGEF-2-containing UNC-73 isoforms, which would not likely be discovered by conventional genetic screening. UNC-73 D1 and D2 appear to function redundantly in pharynx muscle to regulate the rate and strength of pharynx pumping, and in the HSN neurons and vulval muscles to control egg laying. Isoforms C1, C2, E, and F act redundantly within the nervous system to regulate the speed of locomotion. The multiple UNC-73 isoforms containing Rac- and Rho-specific RhoGEF domains therefore have distinct physiological functions. In addition to its previously identified role involving RhoGEF-1 in migrating cells and growth cones, our data indicate that UNC-73 signals through RhoGEF-2 to regulate pharynx and vulva musculature and to modulate synaptic neurotransmission.
Figures
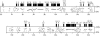





Similar articles
-
Trio's Rho-specific GEF domain is the missing Galpha q effector in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2007 Nov 1;21(21):2731-46. doi: 10.1101/gad.1592007. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17942708 Free PMC article.
-
UNC-73/trio RhoGEF-2 activity modulates Caenorhabditis elegans motility through changes in neurotransmitter signaling upstream of the GSA-1/Galphas pathway.Genetics. 2011 Sep;189(1):137-51. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.131227. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21750262 Free PMC article.
-
ced-10 Rac and mig-2 function redundantly and act with unc-73 trio to control the orientation of vulval cell divisions and migrations in Caenorhabditis elegans.Dev Biol. 2002 Jan 15;241(2):339-48. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0513. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 11784116
-
Genetic analysis of growth cone migrations in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Neurobiol. 2000 Aug;44(2):281-8. J Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10934329 Review.
-
Rho deep in thought.Genes Dev. 2007 Nov 1;21(21):2677-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.1615807. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17974912 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The RHO-1 RhoGTPase modulates fertility and multiple behaviors in adult C. elegans.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 28;6(2):e17265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017265. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21387015 Free PMC article.
-
The RhoGEF trio functions in sculpting class specific dendrite morphogenesis in Drosophila sensory neurons.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033634. Epub 2012 Mar 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22442703 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Growth Cone Polarity, Microtubule Accumulation, and Protrusion by UNC-6/Netrin and Its Receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2018 Sep;210(1):235-255. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301234. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 30045855 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans CARMIL negatively regulates UNC-73/Trio function during neuronal development.Development. 2009 Apr;136(7):1201-10. doi: 10.1242/dev.026666. Epub 2009 Feb 25. Development. 2009. PMID: 19244282 Free PMC article.
-
Elimination of Kalrn expression in POMC cells reduces anxiety-like behavior and contextual fear learning.Horm Behav. 2014 Jul;66(2):430-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Horm Behav. 2014. PMID: 25014196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alam M.R., Johnson, R.C., Darlington, D.N., Hand, T.A., Mains, R.E., and Eipper, B.A. 1997. Kalirin, a cytosolic protein with spectrin-like and GDP/GTP exchange factor-like domains that interacts with peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase, an integral membrane peptide-processing enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 12667-12675. - PubMed
-
- Avery L. and Horvitz, H.R. 1989. Pharyngeal pumping continues after laser killing of the pharyngeal nervous system of C. elegans. Neuron 3: 473-485. - PubMed
-
- Awasaki T., Saito, M., Sone, M., Suzuki, E., Sakai, R., Ito, K., and Hama, C. 2000. The Drosophila trio plays an essential role in patterning of axons by regulating their directional extension. Neuron 26: 119-131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
