Knockdown of Pu.1 by small interfering RNA in CD34+ embryoid body cells derived from mouse ES cells turns cell fate determination to pro-B cells
- PMID: 16141339
- PMCID: PMC1201612
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506218102
Knockdown of Pu.1 by small interfering RNA in CD34+ embryoid body cells derived from mouse ES cells turns cell fate determination to pro-B cells
Abstract
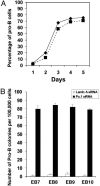
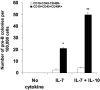
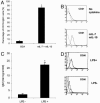
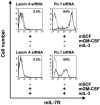
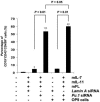
The factors that regulate murine ES cell-derived hematopoietic progenitor cell (HPC) commitment to the B lymphocyte lineage remain unclear. Pu.1 plays an essential role in the development of all lymphoid lineages; however, it also regulates commitment to other blood cell lineages. In this study, we found evidence for early B cell lineage commitment as determined by coexpression of CD19 and CD45R (B220) when Pu.1 expression was knocked down in HPC by specific small interfering RNA (siRNA); moreover, the expression of early B cell factor (Ebf) and paired box protein 5 (Pax-5) transcription factors was induced when cells were treated by Pu.1 siRNA, but not by control siRNA. We also found that siRNA-mediated knockdown of Pu.1 expression was more efficient in generating progenitor B cells (pro-B cells) compared with the more common in vitro method of B lymphoid development by means of coculture of CD34+ embryoid body (EB) cells with OP9 stromal cells. To investigate whether this phenomenon also exists in HPC from other sources, we then knocked down Pu.1 gene expression in CD34+ murine bone marrow cells and found a similar effect of increased production of CD19+CD43+CD45R+ progenitor B cells upon the siRNA-mediated decrease in Pu.1 expression. We conclude that, in early B cell development from ES cell-derived HPC, constitutive Pu.1 expression inhibits the earliest B cell development through repressing early B cell factor and paired box protein 5 expression, although lower levels of Pu.1 expression in HPC play a key role in promoting B cell fate determination.
Figures



References
-
- Keller, G., Lacaud, G. & Robertson, S. (1999) Exp. Hematol. 27, 777-787. - PubMed
-
- Daley, G. Q. (2003) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 996, 122-133. - PubMed
-
- Hamaguchi-Tsuru, E., Nobumoto, A., Hirose, N., Kataoka, S., Fujikawa-Adachi, K., Furuya, M. & Tominaga, A. (2004) Br. J. Haematol. 124, 819-827. - PubMed
-
- Lieber, J. G., Webb, S., Suratt, B. T., Young, S. K., Johnson, G. L., Keller, G. M. & Worthen, G. S. (2004) Blood 103, 852-859. - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto, T. T., Kohata, S., Suzuki, H., Miyazaki, H. & Fujimura, K. (2003) Blood 102, 4044-4051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

