The Set1 methyltransferase opposes Ipl1 aurora kinase functions in chromosome segregation
- PMID: 16143104
- PMCID: PMC1794220
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.021
The Set1 methyltransferase opposes Ipl1 aurora kinase functions in chromosome segregation
Abstract
A balance in the activities of the Ipl Aurora kinase and the Glc7 phosphatase is essential for normal chromosome segregation in yeast. We report here that this balance is modulated by the Set1 methyltransferase. Deletion of SET1 suppresses chromosome loss in ipl1-2 cells. Conversely, combination of SET1 and GLC7 mutations is lethal. Strikingly, these effects are independent of previously defined functions for Set1 in transcription initiation and histone H3 methylation. We find that Set1 is required for methylation of conserved lysines in a kinetochore protein, Dam1. Biochemical and genetic experiments indicate that Dam1 methylation inhibits Ipl1-mediated phosphorylation of flanking serines. Our studies demonstrate that Set1 has important, unexpected functions in mitosis. Moreover, our findings suggest that antagonism between lysine methylation and serine phosphorylation is a fundamental mechanism for controlling protein function.
Figures
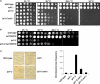
Yeast strains with the indicated genotypes were serially diluted 10-fold, spotted onto YPD medium, and grown at indicated temperatures for 2 days. Growth of four independent ipl1-2 set1 Δ colonies is shown.
Plate spot assays performed as above to test the ability of the set1 G951S mutation to suppress the temperature sensitivity of ipl1-2.
The stability of an artificial minichromosome marked by the SUP11 tRNA gene, which suppresses a defective ade2 allele, was measured in the indicated wild-type and mutant strains. Colony color was scored after 4 days of growth at 25°C. Shown are the averages of two independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations.

Schematic representation of the plasmid shuffle approach used to combine the glc7-127 mutation or the sds22-6 mutation with SET1 deletion. A URA3-marked plasmid bearing the wild-type GLC7 gene was introduced into either glc7-127 or sds22-6 cells. The SET1 gene was then disrupted. Growth of the resulting cells was compared on rich media (YPD) or on 5-FOA-containing media, which selects for cells that have lost the URA3-marked GLC7 plasmid.
Serial dilutions (10-fold) of the indicated strains reveals that deletion of SET1 is synthetic lethal with glc7-127 in the absence of the exogenous wild-type GLC7 allele on 5-FOA-containing media (at 25°C).
Yeast strains with the indicated genotypes were serially diluted 10-fold, spotted onto YPD medium or 5-FOA medium and then grown at indicated temperatures for 3 days. Note the enhanced temperature sensitivity of the sds22-6 set1 Δ cells on 5-FOA-containing media at 30°C and on rich media at 33°C relative to either sds22-6 or set1 Δ single mutants.
Yeast strains with the indicated genotype were again serially diluted 10-fold, spotted onto YPD medium, and then grown at indicated temperatures for 2 days. As expected, the glc7-127 mutation suppresses the ipl1-2 temperature-sensitive phenotype at 32.5°C. Importantly, ipl1-2 glc7-127 set1 Δ triple-mutant cells are viable, and the temperature-sensitive phenotype of ipl1-2 is also suppressed in these cells.
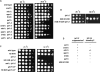
(A, B, and C) Yeast strains with the indicated genotypes were serially diluted 10-fold, spotted onto YPD medium, and grown at the indicated temperatures for 2 days.
(D) Summary of the effects of mutations in genes encoding COMPASS components, PAF1, or the H2B ubiquitylation site on the ipl1-2 phenotype (this work) and H3 K4 methylation (summarized from Krogan et al., [2002], Krogan et al. [2003], and Sun and Allis [2002]).

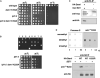
Plate spot assays (as described in previous figures) were used to compare the growth of the indicated strains. Three independent dam1 K194A colonies and three independent ipl1-2 dam1 K194A colonies are shown for comparison.
Eight independent tetrads from sporulation of dam1 K233A/DAM1 heterozygotes (upper panel). In each case, only two spores were recovered. DNA sequencing revealed that these carry the wild-type DAM1 allele (data not shown), indicating that the dam1 K233A mutation is lethal. However, plate spot growth assays (lower panel) reveal that the lethality of dam1 K233A is suppressed by ipl1-2 and also that the temperature sensitivity of ipl1-2 is suppressed by dam1 K233A.
Immunoblot of immunoprecipitates from cells expressing native or HA-tagged Dam1 with either native or myc-tagged Set1. Immunoprecipitation was performed with the anti-HA antisera and the immunoblot was probed with either an anti-myc antibody or an anti HA-antibody, as indicated. *myc-Set1.
(Upper panel) The specificity of the anti-dimethyl K233 Dam1 antisera was confirmed using a dot blot of synthetic Dam1 peptides identical in sequence but containing lysine, dimethyl-lysine, or trimethyl-lysine at the position of K233. Ponceau S staining of a sister blot is shown to confirm equal loading of the peptides. (Lower panel) Wild-type (WT) or K233R mutant HA-tagged Dam1 was immunoprecipitated from wild-type or set1 Δ cells using the anti-HA antibody. An immunoblot of the immunoprecipitates was probed with either anti-HA or the anti-dimethyl K233 Dam1 antisera, as indicated. Immunoprecipitates from a wild-type strain lacking HA-Dam1 is shown as a negative control.
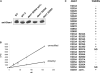
Immunoblot analysis reveals diminishment of slower migrating Dam1 phosphoisoforms (Cheeseman et al., 2002a) upon mutation of IPL1 or mutation of S232, S234, or S235 in Dam1.
Kinase assays demonstrate that a recombinant GST-Ipl1 fusion protein phosphorylates a peptide corresponding to Dam1 amino acids 228–239, indicating that one or more serines flanking K233 are recognized by Ipl1 as substrate in vitro. Shown are the averages of triplicate assays at each amount of peptide used. Error bars represent the standard deviations. Phosphorylation is inhibited by the presence of dimethyl-lysine at the position of K233.
Summary of the effects of the indicated dam1 mutations on cell viability. Note the suppression of the lethality of the K233A mutation by either the S232A or S234A mutations and the cosuppression of the K233A and S235A lethality in K233A S235A double mutants. The S235A lethality is also suppressed in set1 Δ cells. ND: not determined due either to a failure of mutant cells to sporulate (K233A S257A) or failure to recover heterozygous DAM1/dam1 cells (S235A S265D).
References
-
- Cheeseman IM, Anderson S, Jwa M, Green EM, Kang J, Yates JR, 3rd, Chan CS, Drubin DG, Barnes G. Phospho-regulation of kinetochore-microtubule attachments by the Aurora kinase Ipl1p. Cell. 2002a;111:163–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

