Monitoring the mode and tempo of concerted evolution in the Drosophila melanogaster rDNA locus
- PMID: 16143606
- PMCID: PMC1456108
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.047670
Monitoring the mode and tempo of concerted evolution in the Drosophila melanogaster rDNA locus
Abstract
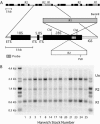
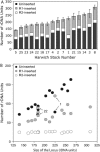
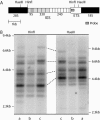
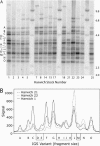
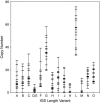
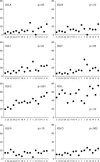
Non-LTR retrotransposons R1 and R2 have persisted in rRNA gene loci (rDNA) since the origin of arthropods despite their continued elimination by the recombinational mechanisms of concerted evolution. This study evaluated the short-term evolutionary dynamics of the rDNA locus by measuring the divergence among replicate Drosophila melanogaster lines after 400 generations. The total number of rDNA units on the X chromosome of each line varied from 140 to 310, while the fraction of units inserted with R1 and R2 retrotransposons ranged from 37 to 65%. This level of variation is comparable to that found in natural population surveys. Variation in locus size and retrotransposon load was correlated with large changes in the number of uninserted and R1-inserted units, yet the numbers of R2-inserted units were relatively unchanged. Intergenic spacer (IGS) region length variants were also used to evaluate changes in the rDNA loci. All IGS length variants present in the lines showed significant increases and decreases of copy number. These studies, combined with previous data following specific R1 and R2 insertions in these lines, help to define the type and distribution, both within the locus and within the individual units, of recombinational events that give rise to the concerted evolution of the rDNA locus.
Figures
References
-
- Burke, W. D., H. S. Malik, W. C. Lathe III and T. H. Eickbush, 1998. Are retrotransposons long-term hitchhikers? Nature 392: 141–142. - PubMed
-
- Burke, W. D., D. Singh and T. H. Eickbush, 2003. R5 retrotransposons insert into a family of infrequently transcribed 28S rRNA genes of Planaria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 20: 1260–1270. - PubMed
-
- Coen, E. S., J. M. Thoday and G. Dover, 1982. Rate of turnover of structural variants in the rDNA gene family of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 295: 564–568. - PubMed
-
- Dover, G., 1994. Concerted evolution, molecular drive and natural selection. Curr. Biol. 4: 1165–1166. - PubMed
-
- Eickbush, T. H., 2002. R2 and related site-specific non-long terminal repeat retrotransposons, pp. 813–835 in Mobile DNA II, edited by N. L. Craig, R. Craigie, M. Gellart and A. M. Lambowitz. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

