Molecular recognition via triplex formation of mixed purine/pyrimidine DNA sequences using oligoTRIPs
- PMID: 16144414
- PMCID: PMC2533713
- DOI: 10.1021/ja0530218
Molecular recognition via triplex formation of mixed purine/pyrimidine DNA sequences using oligoTRIPs
Abstract
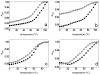
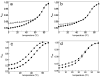
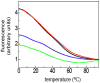
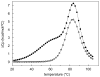
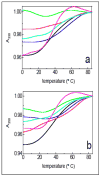
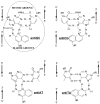
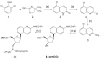
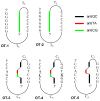
Stable DNA triple-helical structures are normally restricted to homopurine sequences. We have described a system of four heterocyclic bases (TRIPsides) that, when incorporated into oligomers (oligoTRIPs), can recognize and bind in the major groove to any native sequence of DNA [Li et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2084]. To date, we have reported on triplex-forming oligomers composed of two of these TRIPsides, i.e., antiTA and antiGC, and their ability to form intramolecular triplexes at mixed purine/pyrimidine sequences. In the present study, we describe the synthesis and characterization of the antiCG TRIPside and its use in conjunction with antiTA and antiGC to form sequence-specific intra- and/or intermolecular triplex structures at mixed purine/pyrimidine sequences that require as many as four major groove crossovers.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Triple helix forming TRIPside molecules that target mixed purine/pyrimidine DNA sequences.Biochemistry. 2004 Feb 17;43(6):1440-8. doi: 10.1021/bi035648d. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 14769020
-
Synthesis of C-nucleosides designed to participate in triplex formation with native DNA: specific recognition of an A:T base pair in DNA.J Org Chem. 2005 Oct 28;70(22):8764-71. doi: 10.1021/jo0511445. J Org Chem. 2005. PMID: 16238307
-
Solution structure of an antiparallel purine motif triplex containing a T.CG pyrimidine base triple.Structure. 1996 Apr 15;4(4):425-35. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00048-2. Structure. 1996. PMID: 8740365
-
Triplex DNA structures.Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:65-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.000433. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995. PMID: 7574496 Review.
-
Recent improvements in antigene technology.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2003 Dec;7(6):717-26. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2003.10.007. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2003. PMID: 14644181 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting duplex DNA with chimeric α,β-triplex-forming oligonucleotides.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Sep;40(16):8175-85. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks410. Epub 2012 May 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22641847 Free PMC article.
-
Divalent counterion-induced condensation of triple-strand DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Dec 14;107(50):21482-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003374107. Epub 2010 Nov 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21098260 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorobenzene Nucleobase Analogues for Triplex-Forming Peptide Nucleic Acids.Chembiochem. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):e202100560. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100560. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 34889020 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-linking to an interrupted polypurine sequence with a platinum-modified triplex-forming oligonucleotide.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2009 Aug;14(6):873-81. doi: 10.1007/s00775-009-0499-3. Epub 2009 Apr 7. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2009. PMID: 19350290 Free PMC article.
-
Unnatural bases for recognition of noncoding nucleic acid interfaces.Biopolymers. 2021 Jan;112(1):e23399. doi: 10.1002/bip.23399. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Biopolymers. 2021. PMID: 32969496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maher LJ, III, Wold B, Dervan PB. Antisense Res Dev. 1991;1:277–281. - PubMed
-
- Praseuth D, Guieysse AL, Hélène C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1489:181–206. - PubMed
-
- Fox KR. Curr Med Chem. 2000;7:17–37. - PubMed
-
- Dervan PB. Bioorg Med Chem. 2001;9:2215–2235. - PubMed
-
- Kuan JY, Glazer PM. Meth Mol Biol. 2004;262:173–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

