Characterization of toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans strains isolated from humans and domestic cats in the United Kingdom
- PMID: 16145080
- PMCID: PMC1234052
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.9.4377-4381.2005
Characterization of toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans strains isolated from humans and domestic cats in the United Kingdom
Abstract
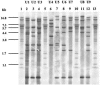
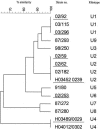
In the United Kingdom there has been a marked increase in the number of human infections caused by toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans. During 2002 and 2003 the organism was also isolated from several domestic cats with bilateral nasal discharge. As C. ulcerans has never previously been isolated from cats, the 16S rRNA gene from three cat isolates was sequenced to confirm their species identities. Fifty clinical isolates from the United Kingdom isolated from 1986 to 2003 and seven cat isolates were characterized by ribotyping to determine whether the ribotypes of the cat isolates were genotypically related to those found for human clinical isolates. For comparison, the genotypes of 11 overseas isolates and 13 isolates from H. R. Carne's collection isolated between 1933 and 1979 were also determined. Strains isolated from domestic cats were found to exhibit the predominant ribotypes observed among human clinical isolates, suggesting that C. ulcerans isolated from cats could be a potential reservoir for human infection.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad, N., N. Gainsborough, and J. Paul. 2000. An unusual case of diphtheria and its complications. Hosp. Med. 61:436-437. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 2000. Three cases of toxigenic Corynebacterium ulcerans infection. Commun. Dis. Rep. Wkly. 10:49. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet, J. M., and N. T. Begg. 1999. Control of diphtheria: guidance for consultants in communicable disease control. Commun. Dis. Public Health 4:242-249. - PubMed
-
- De Zoysa, A., A. Efstratiou, R. C. George, M. Jahkola, J. Vuopio-Varkila, S. Deshevoi, G. Tseneva, and Y. Rikushin. 1995. Molecular epidemiology of Corynebacterium diphtheriae from northwestern Russia and surrounding countries studied by using ribotyping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33:1080-1083. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

